Management by Objectives (MBO) is a strategic approach to management that seeks to enhance organizational performance by precisely defining goals that are mutually accepted by management and employees.
The theory suggests that involving employees in setting goals and action plans fosters engagement and dedication, while also ensuring alignment of objectives throughout the organization.
Management by objectives (MBO)
Management by objectives (MBO), also referred to as management by planning, involves establishing a management information system (MIS) to compare actual performance with defined objectives.
Researchers argue that MBO offers significant advantages, such as enhancing employee motivation and commitment, and facilitating better communication between management and staff.
Despite its benefits, critics highlight a drawback of MBO, namely its excessive focus on goal setting without adequate emphasis on developing a systematic plan to achieve those goals.
Management by Objectives (MBO) was introduced by Peter F. Drucker in 1954 through his book “The Practice of Management,” earning him the title of the Father of MBO. This approach guides subordinates in fulfilling specific objectives within defined timeframes and entails regular evaluations of organizational performance.
As economic shifts have prompted changes in workforce demands, traditional techniques became outdated, giving rise to new methods like MBO. This evolution is vital for organizations to effectively achieve their goals and boost productivity.
Peter Drucker, who introduced the term in his book, outlined key principles for MBO. Objectives are collaboratively set with employees and are designed to be challenging yet attainable.
Regular feedback is provided, with an emphasis on rewarding achievement rather than penalizing failure. The approach also prioritizes personal growth and development over punitive measures for not meeting objectives.
Monitoring and evaluating employee performance and progress against set objectives is a crucial aspect of the Management by Objectives (MBO) approach. When employees are actively engaged in goal setting and decision-making regarding their actions, they are more inclined to fulfill their responsibilities effectively.
MBO Examples
A company has the option to establish different objectives with its staff. For instance, in a call center setting, a Management by Objectives (MBO) target might involve enhancing customer satisfaction by 10% while decreasing call durations by one minute. T
he focus shifts to devising strategies to meet this objective. After determining the approach, it becomes crucial to engage employees, track their advancement, offer feedback, and recognize those who perform well.
MBO examples for company performance
When evaluating if a company has met its objectives, company performance is crucial.
Depending on the overall performance, here are goals you can set:
- Achieve industry leadership.
- Attain a monthly cash flow of $500,000.
- Become a Fortune 500 member.
- Increase Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) to 90%.
- Boost client retention to 92.5%.
Examples of marketing MBOs
Here are examples of Marketing Management by Objectives (MBOs) based on your goals:
- 1,000 new Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) monthly.
- 40% of total revenue from marketing efforts.
- Increase annual product customers by 35%.
- Raise marketing ROI by 7.5%.
- Triple social media following.
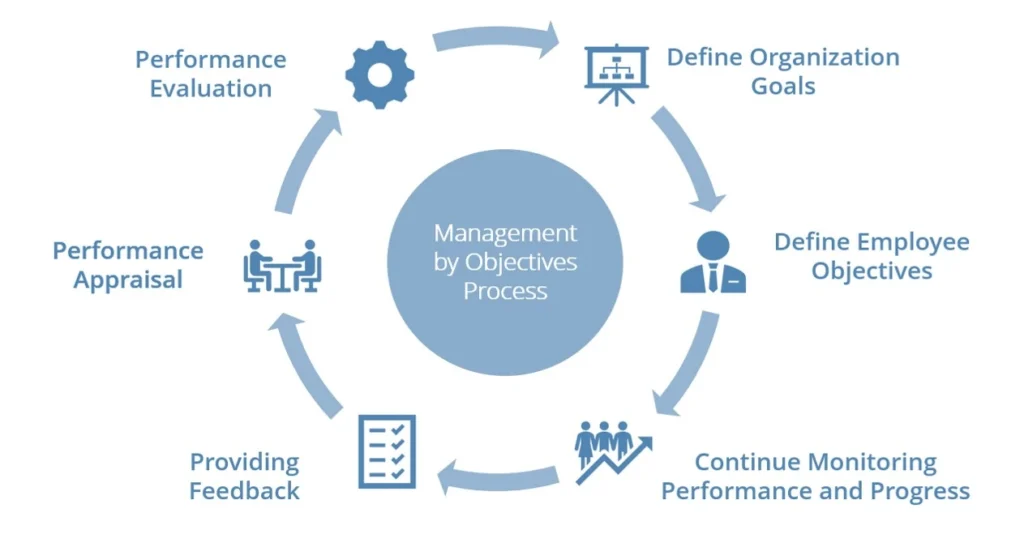
Steps in Management by Objectives (MBO) Process
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a methodical approach that organizations can follow through key steps:
Establish Organizational Goals
Start by defining clear and measurable goals for the organization. These objectives should align with the company’s mission, vision, and strategic priorities. Involve various levels of management in this process to ensure a comprehensive perspective.
Set Employee Objectives
Once the organizational goals are set, managers can collaborate with their team members to establish individual employee objectives. This involves discussing the overall plan, strategies, and resources needed to achieve these goals. Employees provide input on their capabilities, timelines, and feasible targets.
Monitor Performance
Implement a system for continuous monitoring of employee performance and progress towards their objectives. This involves regular feedback sessions, performance reviews, and tracking key metrics to evaluate individual and team achievements. Adjustments to objectives or strategies may be necessary based on ongoing assessments.
Performance Evaluation
In MBO, performance evaluation involves the active participation of managers who are directly involved with the objectives set for their teams or departments. This ensures that evaluations are based on firsthand knowledge and understanding of the objectives and their outcomes.
Providing Feedback
Continuous feedback is central to the MBO approach. It allows employees to track their progress, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary corrections to achieve objectives effectively. This feedback process is supplemented by regular formal evaluation meetings where managers and employees discuss progress, align goals, and provide further feedback for ongoing improvement.
Performance Appraisal
Performance reviews are a standard practice in MBO organizations. These reviews assess employee success in meeting objectives, provide a platform for discussing achievements and challenges, and contribute to ongoing performance improvement efforts.
Advantages of Management by Objectives (MBO)
Empowered Employees
Employees feel a sense of ownership and pride in their work when assigned achievable goals that align with their capabilities.
Enhanced Performance
Tailored goals motivate employees, leading to increased productivity and stronger loyalty to the organization.
Strategic Goal Setting
Management can set goals that drive the overall success of the company, aligning individual efforts with organizational objectives.
Clarity Towards Objectives
Management by Objectives (MBO) facilitates the clear definition of organizational structures and responsibilities. It ensures that authority and responsibility are aligned with job demands, making goal-setting meaningful.
Designing organizational roles based on expected outcomes enhances accountability and helps identify organizational shortcomings.
Better Management Practices
MBO promotes superior management by setting clear goals for actions and individuals, ensuring their achievement, and coordinating resources effectively.
It emphasizes strategic planning over mere task scheduling, encouraging managers to develop strategies for goal accomplishment. Goals also serve as performance standards and aids in effective control.
Enhanced Individual Commitment
An important advantage of MBO is its ability to motivate employees to commit to predetermined goals. Unlike traditional task completion, MBO involves individuals in goal setting, allowing them to present their ideas, discuss options, and contribute to defining objectives. This participative approach fosters individual commitment and engagement.
Establishing Controls
The MBO system facilitates the establishment of efficient controls by setting verifiable targets and monitoring performance against standards.
It helps identify deviations and shortcomings, providing clarity on performance expectations and serving as a tool for effective control.
Improved Communication Channels
MBO encourages collaborative goal-setting between managers and staff, leading to frequent communication about goal progress.
This enhanced communication fosters an environment where employees can raise issues, ask questions, and contribute ideas. Effective communication contributes to increased productivity, better relationships, and job satisfaction.
Motivation and Morale Boost
Participative goal setting and two-way communication in MBO contribute to improved interpersonal relations and recognition at all levels.
Employees feel motivated and have higher morale due to their involvement in goal setting and the opportunities for personal contribution and responsibility acceptance. This participatory approach enhances commitment and morale within the organization.

Disadvantages of Management by Objectives (MBO)
- Neglect of Other Aspects: MBO’s focus on goals may overlook essential aspects such as company culture, work ethics, and opportunities for engagement and contribution.
- Increased Pressure: Employees may experience heightened stress to meet targets within specified timeframes, leading to potential burnout.
- Quality Concerns: The emphasis on meeting targets can incentivize shortcuts and compromise the quality of work.
- Limited Applicability: MBO may not suit all management responsibilities, posing challenges for areas that do not align well with goal-oriented approaches.
- Goal-Setting Complexity: The primary emphasis of the MBO technique is on goal setting, a multifaceted process requiring substantial knowledge. Goals must be measurable and provable to evaluate performance effectively. However, caution is necessary in identifying goals that may be difficult to verify, as immediate target establishment could hold the company accountable.
- Time Consumption: Implementing MBO involves a significant time investment in establishing measurable goals through consensus. This process entails numerous meetings to instill confidence in subordinates regarding goal attainment.
- Short-Term Focus: Many MBO programs tend to prioritize short-term goals, potentially overshadowing long-term objectives. Balancing short-term achievements with long-term goals is crucial to avoid conflicts and ensure proper prioritization.
- Lack of Guidelines: Success in MBO hinges on providing clear guidelines to goal setters. Managers responsible for setting goals must understand organizational policies, strategic planning principles, and their roles to ensure effective goal establishment.
- Organizational Inflexibility: MBO can introduce rigidity as goals are set, making modifications challenging due to potential resistance from subordinates. This inflexibility can hinder adaptability to changing circumstances.
- Increased Paperwork: The administrative aspects of MBO, including newsletters, manuals, and performance reports, can lead to increased paperwork and reduced efficiency in goal management.
What is the purpose of Management by Objectives (MBO)?
The goal of Management by Objectives (MBO) is to utilize quantifiable standards for measuring both company and employee performance.
This approach allows managers to identify areas of improvement and enhance efficiency by comparing actual productivity with predetermined standards.
The key aspect is that both management and employees are aware of and agree upon these standards and objectives, fostering clarity and alignment throughout the organization.
Conclusion
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a strategic approach utilized by managers to guide their employees by establishing clear and measurable goals that both the individual and the organization strive to achieve in the immediate future.
MBO’s core is ensuring employees have clear insight into their roles, duties, and performance standards.
This clarity enables them to see the direct correlation between their actions and the overall success of the organization.
However, for MBO to be effective, it must be carefully planned, decided upon, and controlled within the organizational framework.
Without proper implementation and oversight, there is a risk of employees misinterpreting results and prioritizing short-term, self-centric goals over long-term organizational objectives.
This misalignment can hinder overall performance and hinder the organization’s ability to achieve sustainable success.
Therefore, strategic implementation and clear communication are essential to ensure that MBO serves its purpose of driving collective effort towards organizational success.


