In academic and scholarly writing, proper citation is of utmost importance. One widely used method of citation is the inclusion of footnote citations.
Footnotes are additional pieces of information or references placed at the bottom of a page, allowing readers to access the sources and further explore the cited material.
This article aims to shed light on what footnote citations are, why they are used, and how to create them correctly.
What Are Footnote Citations?
Footnote citations are a form of citation used to provide additional information or reference sources in academic or professional writing.
They appear as superscript numbers within the main text, which correspond to detailed notes placed at the bottom of the page.
These notes contain relevant information about the source, such as the author’s name, title of the work, publication year, and page numbers.
Footnotes can also include explanatory comments, acknowledgments, or additional context.

Purpose of Footnote Citations
Footnote citations serve several purposes in academic writing:
- Giving credit to sources: Footnotes acknowledge the original authors or creators of the cited material, giving credit where it is due. This promotes intellectual honesty and helps avoid plagiarism.
- Providing evidence and supporting claims: Footnotes allow readers to verify the accuracy and credibility of the information presented in the main text. They provide a transparent trail to the sources used, enabling readers to delve deeper into the topic if desired.
- Expanding upon ideas: Footnotes provide an opportunity to include additional information, explanations, or examples that may not fit smoothly into the main text. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Creating Footnote Citations
To create accurate and effective footnote citations, follow these guidelines:
- Placement: Place the superscript number within the main text, typically after the punctuation mark at the end of the sentence.
- Formatting: Format the footnote number as a superscript, either manually or using the formatting tools available in word processing software.
- Content: In the corresponding footnote at the bottom of the page, provide complete and accurate information about the cited source. Include the author’s name, title, publication information (such as the publisher, place, and year), and page numbers if applicable.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in citation style throughout your document. Use a recognized citation style guide, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure uniformity and adherence to academic standards.
Inserting Footnotes in Microsoft Word
- Place your cursor in the location where you want to insert the footnote.
- In Microsoft Word, navigate to the “References” tab located in the toolbar at the top of the screen.
- Within the “References” tab, locate the “Footnotes” group. Click on the “Insert Footnote” button.
- A superscript number will appear at the insertion point in the text, and the cursor will move to the corresponding footnote section at the bottom of the page.
- Type the relevant information for your footnote in the footnote section. This typically includes the author’s name, title, publication information, and page numbers.
- To return to the main text, simply click on the main body of your document, and Word will automatically take you back to the appropriate location.
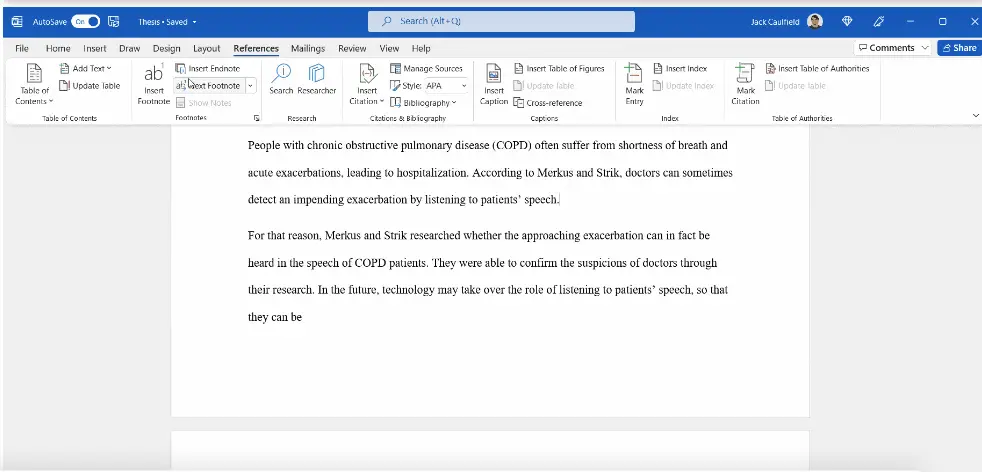
Customizing Footnote Settings in Microsoft Word
- In Word, go to the “References” tab.
- Locate the “Footnotes” group and click on the small arrow in the bottom-right corner to open the Footnote and Endnote dialog box.
- Here, you can customize various settings, such as choosing between footnotes and endnotes, changing the numbering style, adjusting the formatting, and managing the placement of footnotes on the page.
Inserting Footnotes in Google Docs:
- Place your cursor at the point where you want to insert the footnote.
- In Google Docs, navigate to the “Insert” menu at the top of the screen.
- From the dropdown menu, select “Footnote.”
- A superscript number will appear at the insertion point, and the cursor will move to the bottom of the page where you can type your footnote.
- Enter the necessary information for your footnote, such as the author’s name, title, publication details, and page numbers.
Customizing Footnote Settings in Google Docs
- Unfortunately, Google Docs doesn’t offer extensive customization options for footnotes. The default style is typically a numbered superscript format.
- If you need more customization, such as changing the numbering style or altering the appearance, you may need to explore workarounds like manually formatting the footnote section.
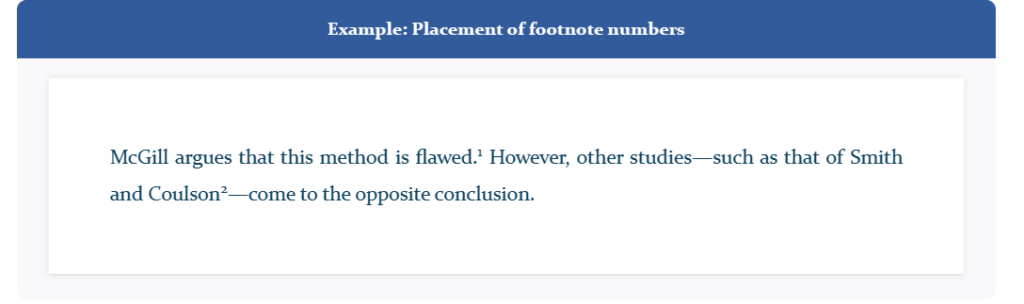
Footnote placement and numbering
Footnotes must be numbered consecutively in the order in which they occur in the paper. Each note should be assigned a unique number; do not use the same number even if you cite the same source multiple times.
Numbers for footnotes are typically added at the end of the relevant clause or sentence. With the exception of when the clause ends in an em dash (—), in which case the number comes before all punctuation. There should not be a space before the number.
Example: Placement of footnote numbers
Footnotes in Chicago style
Footnotes are used for citations in Chicago style (unless you’re using Chicago author-date).
Footnotes can also be used to provide additional information, such as explanations of sources cited, or in-depth elaborations of points raised in the main text.
In Chicago footnotes, you place a footnote at the end of the clause or sentence that has to be cited. When you cite a source for the first time, the footnote has complete information about it, while future citations of the same source contain shortened information.
A bibliography is usually found at the end of a paper. In very short papers, footnote citations may be used alone if your institution allows it.
Example: Chicago footnotes

Chicago suggests adding footnotes using your word processor’s built-in footnote function, but you might need to make a few formatting adjustments manually:
- Each footnote should have an indent at the beginning (before the number).
- At the top of the note, type the number in normal text (not superscript), followed by a period and a space.
- Footnotes should be single-spaced with one blank line between them.
Footnotes in APA Style
APA footnotes are only used to add extra information, since APA in-text citations are appeared in parentheses instead.
You can use them to provide further information, such as additional instances or clarifications; however, you should use them carefully, as APA advises against giving unnecessary information. When necessary, copyright attribution is also given in footnotes.
Example: APA Footnotes

If your word processing software doesn’t automatically create footnotes, APA advises adding an indent at the beginning of each footnote. The superscript footnote number is placed at the beginning of the footnote, followed by a space.
Footnotes in MLA style
MLA footnotes are used to add further information, such as more examples, clarifications of citation practice, or explanations of ideas.
When many citations are required at once, they can be put in a footnote to avoid cluttering the text. MLA in-text citations appear in parentheses, not in notes.
Example: MLA Footnotes

The MLA style guide advises formatting the number at the beginning of the citation in superscript, followed by a space, to automatically insert footnotes using your word processor. Additionally, a new line should be inserted at the beginning of the footnote (before the number).
Conclusion
Footnote citations are an essential component of scholarly writing, providing necessary references, supporting evidence, and additional context.
By using footnote citations correctly, writers demonstrate their commitment to academic integrity and enhance the credibility of their work.
Understanding the purpose and mechanics of footnote citations empowers writers to effectively incorporate external sources while providing readers with a clear pathway to further explore the cited material.



