The Federal Open Market Committee’s (FOMC) target interest rate is referred to as the federal funds rate. The rate at which commercial banks overnight lend and borrow each other’s excess reserves is the aim.
The FOMC, the Federal Reserve System’s decision-making body, gathers eight times a year to determine the target federal funds rate, a component of its monetary policy. This aids in fostering economic growth.
Federal Funds Rate
The interest rate that banks and other depository institutions charge one another when lending money, typically overnight.
Banks are required by law to hold a specific amount of customer money in reserve, where they are not paid interest.
As a result, banks lend money to one another to maintain the right amount while trying to keep as close to the reserve limit as they can without going under it.
What Federal Funds used for?
The federal funds rate, like the federal discount rate, is used to regulate the amount of money that is accessible, which has the effect of reducing inflation and other interest rates.
Borrowing becomes more expensive when the rate is raised. As a result, there will be less money available, which raises the short-term interest rates and controls inflation. The converse happens when the rate is decreased; short-term interest rates fall.
Effects of the Federal Funds Rate
One of the most significant interest rates in the American economy is the federal funds rate. This is because it has an impact on the monetary and financial conditions, which have an impact on important elements of the overall economy such as employment, growth, and inflation.
Due to the fact that lenders frequently base their rates on the prime lending rate, the rate also has an indirect impact on short-term interest rates on credit cards, home loans, and vehicle loans.
Banks charge their most creditworthy borrowers a rate called the prime rate, which is also impacted by the federal funds rate.
Ongoing monitoring of the federal funds rate is done by investors. Changes in the target rate often have a big impact on the stock market.
For instance, a slight drop in the rate can cause the market to soar higher as business borrowing expenses decrease. To try to gain a sense of where the target rate may be headed, many stock analysts pay close attention to statements made by FOMC members.
How Does the Federal Funds Rate Perform?
The interest rate that banks charge one another to lend or borrow excess reserves overnight is known as the federal funds rate.
Banks are required by law to maintain a minimum amount of reserves in relation to their deposits.
A Federal Reserve Bank is where this reserve requirement is kept. When a bank has more reserves than it needs, it could lend those funds to other banks that have discovered a reserve deficiency overnight.
How Is the Federal Funds Rate Determined?
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) typically gathers eight times a year to decide on the federal funds rate. Economic indicators that convey information about the nation’s economic health, such as the core inflation rate and the durable goods orders report, have an impact on these rates.
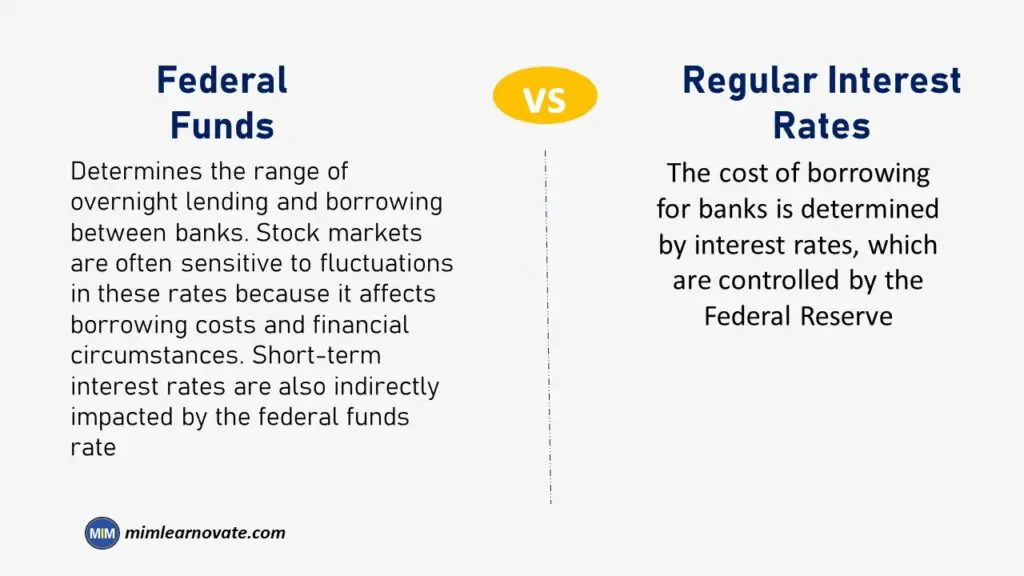
What Is the Difference Between the Federal Funds and Regular Interest Rates?
One of the most significant financial indicators in the United States is the federal funds rate, along with interest rates.
The main difference is that the federal funds rate determines the range of overnight lending and borrowing between banks. Stock markets are often sensitive to fluctuations in these rates because it affects borrowing costs and financial circumstances. Short-term interest rates are also indirectly impacted by the federal funds rate. In contrast, the cost of borrowing for banks is determined by interest rates, which are controlled by the Federal Reserve.



