What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a document that summarizes existing research related to your topic and adds your own insights about it.
It is important for three reasons:
- Firstly, a literature review can improve the quality of your final research paper because it forces you to think critically about the research that has already been done on the topic.
- Literature reviews are especially useful when creating new research, as they help you avoid repeating old ideas and instead focus on new areas of study. A good literature review will also help you when writing your final thesis or dissertation by providing context and referring back to sources that might otherwise have been hard to find.
- Finally, a good literature review will also prove useful when it comes time to apply for jobs or graduate school because it showcases not just your ability to conduct research, but also your ability to understand and synthesize what others have discovered.
A literature review is an investigation of scholarly articles on a particular subject. It gives you a summary of the state of the art and enables you to pinpoint pertinent theories, methods, and research gaps.
What is the aim of a literature review?
A literature review is usually required while writing a thesis, dissertation, or research paper in order to place your findings within the body of existing knowledge.
With the literature review, you can:
- Show that you are knowledgeable about the subject and its academic background.
- Develop a research methodology and theoretical framework.
- Place your work in the context of other scholars and theorists.
- Describe how your research addresses a gap or advances a discussion.
- Assess the state of the field’s research and show that you are aware of the scholarly arguments around it.
5 Steps to Write a Literature Review
In order to write a literature review, you must locate pertinent works (such as books and journal articles), analyse them critically, and then explain your findings.
There are five essential steps.
- Search
- Evaluate
- Identify
- Outline
- Write
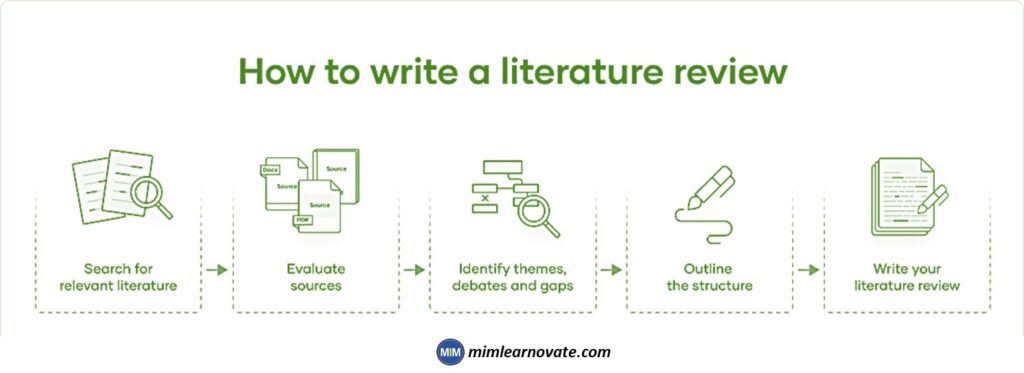
Step 1: Search for Relevant Literature
- Define your topic
- Develop your research problem and questions
- Make a list of Keywords

You need to define your topic before you begin searching for literature.
The first step in writing any research paper is finding relevant literature according to the topic that you have choose. This includes journal articles, books, and online sources.
It is important to be as inclusive as possible when searching for literature because the more sources you have to draw upon, the broader and more complete your review will be. When searching for literature, pay attention to the journal articles and books you find. Make sure that these sources have been published in the last five years.
Next step is to develop your research problem, and questions.
Finally, pay attention to the title of each source, its author(s), and keywords.
Next you need to Make a list of keywords. Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts, or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms, and related terms.
Use your keywords, to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases, to search for journals, and articles, include.
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- JSTOR
- EBSCO
- Medline, (life sciences, biomedicine)
- EconLit, (economics)
- Inspec, (physics, engineering, computer science)
- Project Muse (humanities, social sciences)
These will help you understand the source and decide if it is relevant to your paper.
Step 2: Evaluate and select sources
After finding a large number of sources, it is important to evaluate and select them. This is because you will not be able to include every single source in your paper.
There are two main questions you should ask yourself when selecting sources for your literature review:
- Is it relevant?
- Is it high quality?
Relevance is important because it allows you to focus on the most pertinent research, avoiding sources that are too specific or dated.
High-quality sources are important because they help support your argument and add legitimacy to your paper. To determine the quality of sources, consider the reputation of the author, the source’s publication date (again, try to avoid really old sources), and its accessibility.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything, that has been written, on the topic. you’ll have to evaluate, which sources are most relevant, to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself.

- What questions are addressed?
- What are the key concepts?
- What are the key theories, and methods?
- What are the results, and conclusions?
- How does it relate to other studies?
- What are the key insights, and arguments?
- What are the research‘s benefits and drawbacks?
Once you’ve selected the sources you want to use, you can start to include them in your paper. The best way to do this is by creating a “notes” section in your paper where you can write down citations and direct quotes from literature. This makes it easier to avoid plagiarism and helps you when it comes time to cite your sources.
Step 3: Identify issues, and gaps
After you’ve chosen the sources for your literature review, the next step is to identify issues, and gaps in the research around your topic.
This process can be done in one of two ways:
You can either read each source and make a list of issues, and gaps as you go, or you can do this with all of the sources at once.
The first method is a bit slower, but it allows you to keep track of which issues are coming from which sources.
The second method is faster, but it is important to remember that you might miss something if you’re reading through all of the sources at once.
Once you’ve identified these elements in the literature, the next step is to reflect on them and include them in your paper. This is because these elements are a useful way to frame your own research and provide a context for your arguments.
To begin organizing, your literature review’s argument, and structure, you need to understand the connections, and relationships, between the sources, you’ve read. Based on your reading, and notes, you can look for.

- Trends, and patterns—In theory, method, or results, do certain approaches, become more, or less, popular over time.
- Themes.—It includes what questions, or concepts, recur across the literature.
- Debates—-conflicts, and contradictions. Where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications—-Are there any influential theories, or studies, that changed the direction, of the field?
- Research Gaps—– What is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses, that need to be addressed?
Step 4: Outline structure of your literature review
Once you’ve found and selected sources, identified issues, and gaps in the literature, and read through each source to get a better sense of its contents, you can use this information to outline your literature review.
There are various approaches, to organize the body, of a literature review. You should have a rough idea, of your strategy, before you start writing.
Depending on the length, of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies.

- Chronological
In this strategy, Organize your literature review by time.
- Thematic
In this strategy, Organize your literature review by theme.
- Methodological
In this strategy, Organize your literature review by methodology.
- Theoretical
In this strategy, Organize your literature review by theoretical approach.
Once you’ve chosen the structure, use your notes to sketch out the points you want to make in your literature review.
This will help you organize your thoughts and make sure that everything you want to say is included. You can also use existing models and frameworks as a guide for your own paper.
Step 5: Write your literature review
Once you’ve chosen your structure and outlined all of your points, it’s time to write your literature review.
Your literature review should have an introduction, a major body, and a conclusion just like any other academic paper.
Depending on the objective of your literature review, you should decide what to include in each.

Introduction
The introduction, should clearly establish the focus, and purpose, of the literature review.
Body
Analyze the literature. You may choose to break up the content of your literature review into subsections depending on its length.
For each theme, timeframe, or methodological approach, you can use a subheading.
Conclusion
You should highlight the relevance of the major discoveries you have drawn from the literature and summarize them in the conclusion.
When writing your literature review, make sure to use direct quotes from sources and citations when appropriate. This will not only help you avoid plagiarism, but it will also prove that your review is legitimate and not just your own words.
Finally, be sure to proofread your paper and check for any errors. This is important because it shows your reader that you care about quality and want to produce the best work you can.
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about research methodology.
Statistics
Methodology
- Research Methods
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research
- Survey Research
- Conclusive Research
- Descriptive Research
- Cross-Sectional Research
- Theoretical Framework
- Conceptual Framework
- Triangulation
- Grounded Theory
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Mixed Method
- Correlational Research
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Stratified Sampling
- Ethnography
- Ghost Authorship
- Secondary Data Collection
- Primary Data Collection
- Ex-Post-Facto
Research
- Table of Contents
- Dissertation Topic
- Synopsis
- Thesis Statement
- Research Proposal
- Research Questions
- Research Problem
- Research Gap
- Types of Research Gaps
- Variables
- Operationalization of Variables
- Literature Review
- Research Hypothesis
- Questionnaire
- Abstract
- Validity
- Reliability
- Measurement of Scale
- Sampling Techniques
- Acknowledgements




1 Comment
Awesome issues here. I’m very happy to peer your article.
Thank you a lot and I am looking ahead to touch you.
Will you please drop me a e-mail?