The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, commonly known as SPSS, is a powerful software program widely used in various fields for statistical analysis and data management.
Whether you are a student, researcher, or professional, having a good understanding of SPSS can greatly enhance your ability to analyze and interpret data effectively. In this guide, we will provide you with a comprehensive overview of SPSS, its key features, and how to utilize it for your data analysis needs.
What is SPSS?
SPSS is a software package developed by IBM that provides a range of tools and techniques for statistical analysis. Initially designed for social science research, SPSS has expanded its functionality and is now used across various disciplines. It offers a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to both beginners and experienced data analysts.
Key Features of SPSS:
- Data Management: SPSS allows you to import, clean, and manipulate data efficiently. You can merge datasets, recode variables, handle missing data, and perform data transformations.
- Descriptive Statistics: SPSS provides a wide range of descriptive statistics, such as measures of central tendency, variability, and frequency distributions, allowing you to summarize and understand your data.
- Inferential Statistics: With SPSS, you can perform various inferential statistical tests, including t-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis, chi-square tests, and more. These tests help you draw conclusions and make inferences about populations based on sample data.
- Data Visualization: SPSS offers interactive charts, graphs, and plots to visually represent your data. This feature enables you to explore patterns, relationships, and trends in your data more effectively.
- Syntax Language: SPSS provides a syntax language that allows you to write scripts and automate repetitive tasks. This feature enhances the reproducibility of your analyses and provides a more efficient workflow.
- Customized Reporting: SPSS allows you to create customized reports and export your results to other formats, such as Microsoft Excel and PDF. This feature facilitates sharing and presentation of your findings.
- Community Support and Resources: SPSS has a large user community, which means there are abundant resources available for learning and troubleshooting. Users can access forums, online tutorials, textbooks, and professional support to enhance their understanding and proficiency with the software.
Use of SPSS
SPSS is widely used in academic research, market research, healthcare, government agencies, and other industries that require statistical analysis. It continues to be a popular choice due to its comprehensive set of features, ease of use, and strong analytical capabilities.
SPSS: Supported File Format
SPSS has an ability to open each file format used for structured data, such as:
- STATA and SAS
- spreadsheets from OpenOffice or MS Excel
- plain text files (.csv or .txt)
- Relational database
Getting Started with SPSS
- Installation: Obtain a licensed copy of SPSS from IBM’s website or through your institution. Follow the installation instructions provided by IBM to set up the software on your computer.
- Data Import: Import your data into SPSS from various sources, including spreadsheets, databases, and text files.
- Data Cleaning: Clean your data by checking for missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies. Handle missing data appropriately based on your research requirements.
- Variable Definition: Define your variables, including variable types (numeric or categorical) and measurement levels (nominal, ordinal, or scale).
- Data Analysis: Perform the desired statistical analyses based on your research questions and objectives. Use the appropriate tools and techniques available in SPSS to obtain meaningful insights from your data.
- Data Visualization: Utilize SPSS’s data visualization features to create charts, graphs, and plots that effectively communicate your findings.
- Reporting: Generate customized reports and export your results in a format that suits your needs. Provide clear explanations and interpretations of the statistical analyses conducted.
Pros and Cons of SPSS
Certainly! Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS):
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| User-friendly interface | Steeper learning curve for advanced features |
| Comprehensive set of statistical procedures | Limited support for some advanced analyses |
| Efficient data management capabilities | You need to buy the software |
| Robust data visualization options | Requires computational resources |
| Syntax language for automation and reproducibility | Less flexible for non-standard analyses |
| Extensive community support and resources | Limited compatibility with other software |
| Customizable reporting and export options | Requires proper training for optimal use |
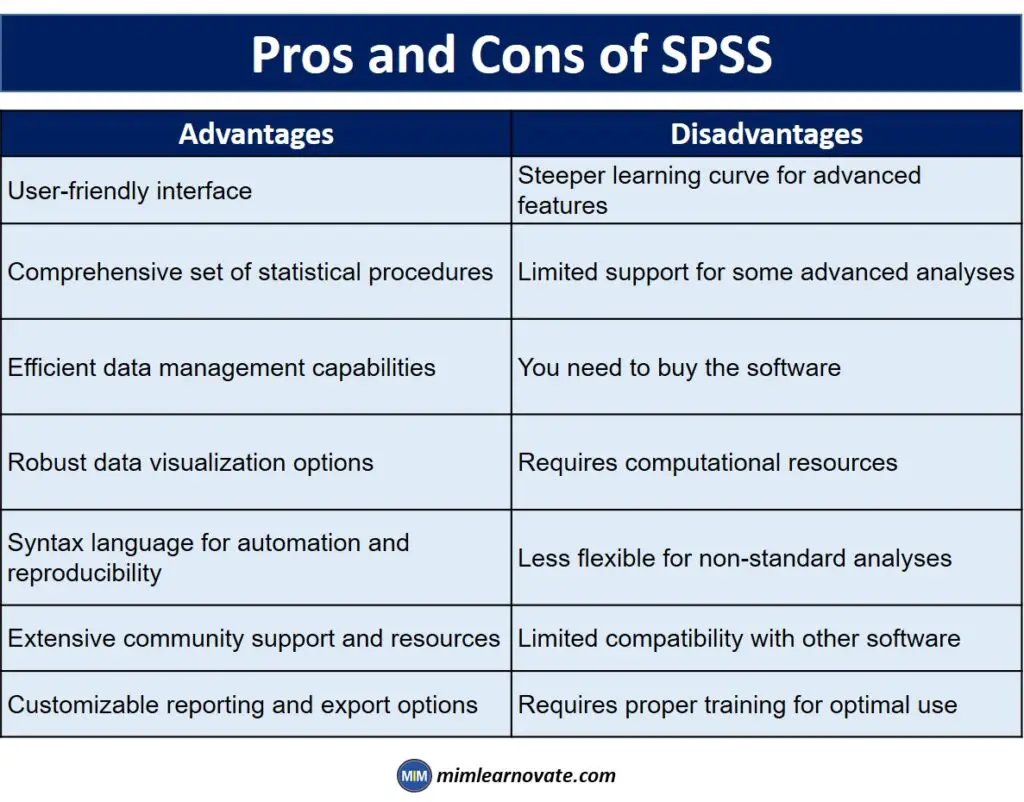
It’s important to note that while SPSS offers numerous advantages for statistical analysis and data management, it also has certain limitations and considerations.
Understanding these pros and cons can help you make informed decisions about whether SPSS is the right tool for your specific data analysis needs.
Use of IBM SPSS in Industries
IBM SPSS is a widely used statistical software package that finds application in various industries. Here are some industries where IBM SPSS is commonly utilized:
- Academia and Education: IBM SPSS is extensively used in academic institutions and research organizations for data analysis and statistical research across various disciplines.
- Market Research: SPSS is employed by market research firms to analyze survey data, conduct consumer behavior studies, and generate insights for strategic decision-making.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: SPSS is utilized in healthcare and pharmaceutical industries for clinical research, patient data analysis, and drug development studies.
- Government and Public Sector: Many government agencies use SPSS for policy analysis, social science research, and data-driven decision-making.
- Finance and Banking: SPSS is used in financial institutions for data analysis related to risk assessment, fraud detection, and market research.
- Manufacturing and Retail: SPSS aids in analyzing customer data, forecasting demand, and improving operational efficiency in the manufacturing and retail sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions
1- Is SPSS qualitative or quantitative?
Quantitative data analysis is done with the aid of software like SPSS. Data that is qualitative shows the characteristics or qualities of the data. It gathers information through observations, questionnaires, and interviews.
2- Why SPSS is better than Excel?
Software for statistical analysis is SPSS, whereas spreadsheet software is Excel. Excel can perform statistical analysis, but SPSS has greater power. The manipulation of data is simple with SPSS. However, if you use Excel, you must put up a lot of effort.
3. Can you get SPSS for free?
IBM SPSS is licensed software that is available for purchase. Because of this, it is not free to use. However, if you’re a student or a staff member, you can ask a reputable college or organization to provide you access.
4. Why do you prefer SPSS over other software>
It’s important to note that different software tools have their own strengths and weaknesses. The preference for SPSS over other software depends on the specific needs of the user, the nature of the data being analyzed, and the research objectives.
Researchers should carefully consider their requirements and explore different software options to determine the best fit for their analysis.
Conclusion:
SPSS is a valuable tool for statistical analysis and data management. It provides a user-friendly interface, a wide range of statistical procedures, and data visualization capabilities.
By mastering SPSS, you can enhance your ability to analyze data, draw meaningful conclusions, and make informed decisions based on evidence. Whether you are a student, researcher, or professional, incorporating SPSS into your data analysis toolkit can greatly benefit your work and contribute to more robust and accurate results.
Remember, practice and hands-on experience are crucial for becoming proficient in SPSS. Explore the software, try different analyses, and consult additional resources,
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about research methodology.
Statistics
- PLS-SEM model
- Principal Components Analysis
- Multivariate Analysis
- Friedman Test
- Chi-Square Test (Χ²)
- T-test
- SPSS
- Effect Size
- Critical Values in Statistics
- Statistical Analysis
- Calculate the Sample Size for Randomized Controlled Trials
- Covariate in Statistics
- Avoid Common Mistakes in Statistics
- Standard Deviation
- Derivatives & Formulas
- Build a PLS-SEM model using AMOS
- Principal Components Analysis using SPSS
- Statistical Tools
- Type I vs Type II error
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Microsoft Excel and SPSS
- One-tailed and Two-tailed Test
- Parametric and Non-Parametric Test
Methodology
- Research Methodology Quiz MCQ
- Research Methods
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research
- Survey Research
- Conclusive Research
- Descriptive Research
- Cross-Sectional Research
- Theoretical Framework
- Conceptual Framework
- Triangulation
- Grounded Theory
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Mixed Method
- Correlational Research
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Stratified Sampling
- Ethnography
- Ghost Authorship
- Secondary Data Collection
- Primary Data Collection
- Ex-Post-Facto
Research
- Table of Contents
- Dissertation Topic
- Synopsis
- Thesis Statement
- Research Proposal
- Research Questions
- Research Problem
- Research Gap
- Types of Research Gaps
- Variables
- Operationalization of Variables
- Literature Review
- Research Hypothesis
- Questionnaire
- Abstract
- Validity
- Reliability
- Measurement of Scale
- Sampling Techniques
- Acknowledgements


