Have you ever wondered how researchers develop a solid foundation for their studies?
The answer lies in the construction of a theoretical framework. In the realm of research, a theoretical framework provides a conceptual structure that guides the investigation, helping researchers organize their thoughts and approach their work systematically.
In this article, you will learn about theoretical frameworks, explore their importance, and provide you with some concrete examples to enhance your understanding.
When embarking on a research journey, scholars need a roadmap to guide them through the complexities of their study.
This roadmap comes in the form of a theoretical framework, a vital tool that provides structure and direction.
By establishing a theoretical framework, researchers can lay the groundwork for their investigations and ensure coherence and clarity in their findings.
9 Theoretical Framework Examples
What Is a Conceptual Framework? | Examples
Acknowledgements for PhD Thesis and Dissertations | Examples
Do All References in a Reference List Need to Be Cited in Text?
What is Theoretical Framework?
A theoretical framework plays a vital role in academic research, providing a solid foundation for developing arguments and shaping the direction of your work.
It involves a comprehensive review of existing theories that aim to explain phenomena, establish connections, and make predictions. By incorporating a theoretical framework, you demonstrate the relevance and grounding of your research topic in established ideas.
Components of a Theoretical Framework
To better comprehend the construction of a theoretical framework, let’s explore its key components:
1. Conceptual Definitions
Before diving into the research, it is crucial to define the key concepts that underpin the study. These conceptual definitions establish a common understanding of the variables and ensure consistency throughout the research process.
2. Review of Existing Literature
A thorough review of existing literature is an essential step in constructing a theoretical framework. By examining previous studies and scholarly works related to the research topic, researchers can identify gaps, establish a context for their study, and build upon existing knowledge.
3. Theoretical Constructs
Theoretical constructs are the building blocks of a theoretical framework. These constructs are abstract concepts or variables that researchers believe to be important in explaining the phenomenon under investigation. They provide a theoretical foundation upon which hypotheses or research questions are formulated.
4. Hypotheses or Research Questions
Based on the identified theoretical constructs, researchers develop hypotheses or research questions that guide their study. These statements or queries serve as the driving force behind the investigation and provide a framework for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
The Importance of a Theoretical Framework
A well-developed theoretical framework is crucial for several reasons:
- Organizing Thoughts: A theoretical framework helps researchers organize their thoughts and ideas, ensuring a systematic approach to their study.
- Providing Structure: It provides a structure that connects the research objectives, variables, and concepts, fostering coherence and clarity in the research process.
- Enhancing Validity: A robust theoretical framework strengthens the validity of the research findings by ensuring that the study is grounded in existing knowledge and established theories.
- Guiding Data Collection and Analysis: It guides researchers in selecting appropriate methods for data collection and analysis, enabling them to derive meaningful insights from their study.
Basis of Theoretical Framework
The theoretical framework is based on
- problem statement
- research questions
- literature review
Read More:
Mastering the Art of “et al.”: A Comprehensive Guide in APA, MLA, and Chicago Style
Secondary Data Collection Methods
What is Primary Data Collection? Types, Advantages, and Disadvantages
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples
Sample problem statement and research questions
The boutique downtown is facing a significant challenge as many of their online customers do not make repeat purchases, which hampers the growth of the store. The management aims to enhance customer loyalty by improving customer satisfaction, with the objective of increasing the number of returning customers.
To address this problem, the following problem statement, objective, and research questions have been identified:
Problem: The lack of return purchases from online customers. Objective: To increase the quantity of returning customers. Research question: How can the satisfaction of online customers be enhanced to foster an increase in return customers?
The central concepts of “customer loyalty” and “customer satisfaction” hold crucial importance in this study, particularly regarding their correlation with customer retention. It is necessary to define these concepts within the theoretical framework and explore relevant theories that shed light on the relationship between these variables.
Some sub-questions to consider may include:
- What is the association between customer loyalty and customer satisfaction?
- What is the current level of satisfaction and loyalty among the boutique’s online customers?
- What factors influence the satisfaction and loyalty of online customers?
By addressing these sub-questions, a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between customer satisfaction, loyalty, and the potential factors affecting them can be developed.
Sample theoretical framework
Below is a simplified example illustrating how theories on customer satisfaction can be described and compared within a thesis or dissertation:
Customer satisfaction:
Customer satisfaction, as defined by Thomassen (2003, p. 69), refers to “the perception of the customer resulting from consciously or unconsciously comparing their experiences with their expectations.” Kotler & Keller (2008, p. 80) further elaborate on this definition, stating that customer satisfaction is determined by “the extent to which an individual is pleased or disappointed with the observed performance of a product in relation to their expectations.”
If the product’s performance falls short of expectations, it leads to customer dissatisfaction, while meeting or exceeding expectations results in satisfied customers (Kotler & Keller, 2003, p. 80).
Zeithaml and Bitner (2003, p. 86) offer a slightly different definition, emphasizing that “satisfaction is the consumer fulfillment response, a judgment that a product or service feature, or the product or service itself, provides a pleasurable level of consumption-related fulfillment.” Their focus lies on achieving a specific satisfaction level related to the act of purchasing.
Considering the emphasis on unconscious perception in the boutique’s mission statement, Thomassen’s definition is most relevant for this study.
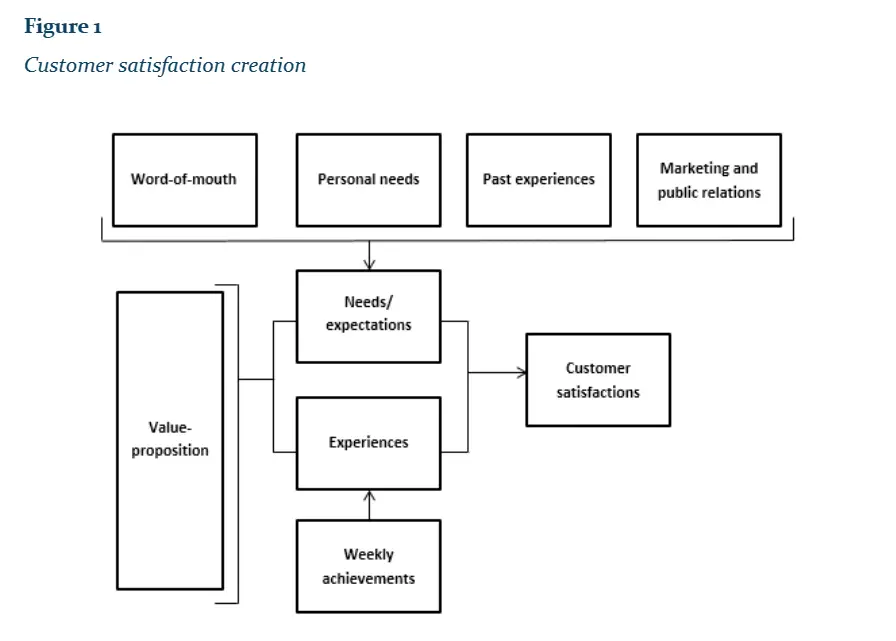
Thomassen’s Customer Satisfaction Model :
This model demonstrates that the value proposition, word-of-mouth, personal needs, past experiences, and marketing and public relations influence customers’ expectations and satisfaction levels.
By comparing their experiences with their expectations, the satisfaction level of customers is determined. This model is instrumental in evaluating the extent of customer satisfaction and identifying areas where improvements can be made.
It is important to note that for a more thorough analysis, additional definitions can be compared, and theories and ideas from key authors can be discussed in greater detail, along with providing multiple models to illustrate different concepts.
Read More:
What is a Thesis Statement? | 10 Examples [2023]
4 Research Proposal Examples | Proposal Sample
How to Choose a Dissertation Topic That Sets You Up for Success?
How to Use ChatGPT to Write a Literature Review With Prompts
How to Write a 10 and 20-Page Research Paper in One Night
How to Develop a Theoretical Framework?
When it comes to writing a theoretical framework, there are several steps you can follow to create your own unique framework while maintaining academic integrity.
These steps will guide you in structuring and developing a robust theoretical framework that aligns with your research objectives. Let’s explore these steps in detail:
1. Identify the Research Problem
Clearly define the research problem or question that your study aims to address. This will serve as the starting point for developing your theoretical framework.
Begin by identifying the key concepts from your problem statement and research questions. It is essential to clearly define these concepts and provide a comprehensive understanding of their meaning within your research context. By doing so, you establish a solid foundation for your theoretical framework.
For example, consider a scenario where a boutique downtown is facing the challenge of low customer retention among online shoppers. Key concepts in this case could include “customer loyalty” and “customer satisfaction.” Your theoretical framework should define these concepts and explore relevant theories that elucidate the relationship between these variables.
2. Conduct a Literature Review
Thoroughly review existing literature related to your research topic. This will help you identify relevant theories, concepts, and gaps in knowledge that your study can contribute to.
Conduct a thorough literature review to evaluate and understand existing theories related to your key concepts. Examine how different researchers have defined these concepts and established connections between them.
It is crucial to note that a literature review and a theoretical framework are distinct components. While a literature review evaluates existing sources, a theoretical framework focuses on the theoretical underpinnings of your work.
3. Choose Relevant Concepts and Theories
Based on your literature review, select the concepts and theories that align with your research objectives. These will form the basis of your theoretical framework.
While discussing these theories, justify your selection and explain why certain theories are more suitable for your research than others. You can even combine theories from different fields to construct a unique framework tailored to your specific topic.
Show how your research contributes to existing knowledge
In addition to summarizing and discussing existing theories, your theoretical framework should highlight how your research expands upon or utilizes these ideas. Demonstrate how your project adds value to the existing body of knowledge by:
- Testing a theory in a previously unexplored context
- Using an existing theory as a framework for interpreting your results
- Critiquing or challenging an established theory
- Integrating multiple theories in a novel or unique way
By showcasing how your research builds upon existing theories, you provide a clear rationale for your study and establish its significance within the research landscape.
4. Formulate Hypotheses
Using the chosen concepts and theories, formulate hypotheses or research questions that guide your study. These statements will direct your data collection and analysis efforts.
5. Refine and Revise the Theoretical Framework
As your research progresses, continuously refine and revise your theoretical framework to ensure its alignment with emerging findings and new insights.
Structuring theoretical framework
When structuring your theoretical framework, consider the guidelines provided by your department or institution. While there are no fixed rules.
When structuring your theoretical framework, you can consider the following approaches:
- Draw on research questions: Structure each section around a research question or key concept.
- Organize by theory cluster.
- Organize by date.
Properly citing your sources throughout your theoretical framework is vital to avoid plagiarism and uphold academic integrity.
By following these steps and adhering to sound academic practices, you can create a well-structured and comprehensive theoretical framework that strengthens your research paper, thesis, or dissertation.
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about research methodology.
Statistics
- PLS-SEM model
- Principal Components Analysis
- Multivariate Analysis
- Friedman Test
- Chi-Square Test (Χ²)
- T-test
- SPSS
- Effect Size
- Critical Values in Statistics
- Statistical Analysis
- Calculate the Sample Size for Randomized Controlled Trials
- Covariate in Statistics
- Avoid Common Mistakes in Statistics
- Standard Deviation
- Derivatives & Formulas
- Build a PLS-SEM model using AMOS
- Principal Components Analysis using SPSS
- Statistical Tools
- Type I vs Type II error
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Microsoft Excel and SPSS
- One-tailed and Two-tailed Test
- Parametric and Non-Parametric Test
Methodology
- Research Methods
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research
- Survey Research
- Conclusive Research
- Descriptive Research
- Cross-Sectional Research
- Theoretical Framework
- Conceptual Framework
- Triangulation
- Grounded Theory
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Mixed Method
- Correlational Research
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Stratified Sampling
- Ethnography
- Ghost Authorship
- Secondary Data Collection
- Primary Data Collection
- Ex-Post-Facto
Research
- Table of Contents
- Dissertation Topic
- Synopsis
- Write Best Review Paper to Get More Citation
- Review Article
- Thesis Statement
- Research Proposal
- Research Questions
- Research Problem
- Research Gap
- Types of Research Gaps
- Variables
- Operationalization of Variables
- Literature Review
- Research Hypothesis
- Questionnaire
- Abstract
- Validity
- Reliability
- Measurement of Scale
- Sampling Techniques
- Acknowledgements