Today, qualitative and quantitative trading/investing types predominate, with many hybrids in between.
This article will show the main difference qualitative trading and quantitative trading with the help of examples.
To develop a trading strategy that suits their comfort level, traders might combine several qualitative and quantitative trading elements. Making a trading system that has both mechanical and discretionary components can be strong and offer some of the greatest features of both types of strategies.
Qualitative Trading
The goal of qualitative analysis is to comprehend human behavior from the viewpoint of the information researcher. It searches for dynamics in a fully realized reality. Human behavior can be learned about through observation, historical research, and interviews.
Through descriptions and themes, data is analyzed. The way that data is interpreted and reported depends on the researcher’s viewpoint and the patterns they identify.
A qualitative analyst considers not just the numbers but also the subjective aspects of the organisation, such as management quality, corporate governance practises, ethics, brand value, reputation, long-term plans, and so on.
The quality of the asset is truly the focus of the quantitative approach. Investors frequently associate Warren Buffett and this strategy since they are familiar with Buffett’s reputation for purchasing “wonderful companies” at value prices.
As a result, according to research, qualitative investors and funds make more concentrated bets and pay closer attention to the underlying asset.
A qualitative trader uses techniques based on news-driven patterns that induce emotional reactions in buyers and sellers in order to trade based on the emotions of traders and investors. They hunt for market behaviors that are emotionally driven.
They are primarily discretionary traders who try to profit from other dealers’ emotional reactions. Qualitative traders gain an advantage by forming opinions based on their experience and the patterns they observe.
Example of Qualitative Trading
It has been recently observed price increases on many of the home items people purchase. That must indicate that inflation has increased since last year, which makes people think that interest rates will also increase. It is highly likely that stock prices will decline as a result of the higher interest rates.
Quantitative Trading
Quantitative analysis uses statistics to discover facts about social behavior. It makes the assumption that reality is fixed and measurable. Data are gathered by measurement and quantification. Data comparisons and noticed statistical patterns are used to analyze the data. Data is given using a statistical analysis filter.
Back testing, chart studies, and quantified statistical analysis are all used by quantitative traders. To trade reoccurring price patterns in the markets, quantitative traders are generally mechanical traders who employ quantified entrances, exits, and position size.
Quantitative traders gain an advantage by mechanically adhering to their strategy and the price movement in spite of their beliefs, expectations, emotions, or ego.
An objective analysis built on quantifiable data is known as a quantitative analysis. For instance, it might be the frequency of a setup, the success rate of a particular trading strategy, the standard deviation of it, or the use of Bollinger bands.
All of this is taken into consideration as a quantitative analyst creates a set of guidelines for their next moves. For example, if the strategy demands that a stock meet 20 of 30 criteria, it will disregard any stock that meets 19 criterion or less.
The fact that quantitative analysts can take advantage of computing power is a huge perk of their position. It is due to the fact that numbers, rather than human judgement, are used to make decisions.
In other words, programmers may send this set of instructions to a computer and have it automatically carry them out in a matter of fractions of a second because the parameters have already been set.
Example of Quantitative Trading
I conducted research to determine the precise amount of price increases after observing that various household items had increased in price. Then, I’ll research how much 1% inflation will impact stock prices. In order to determine whether the company is continually increasing, I must also compare the company’s earnings report with those from prior quarters before placing the trade.
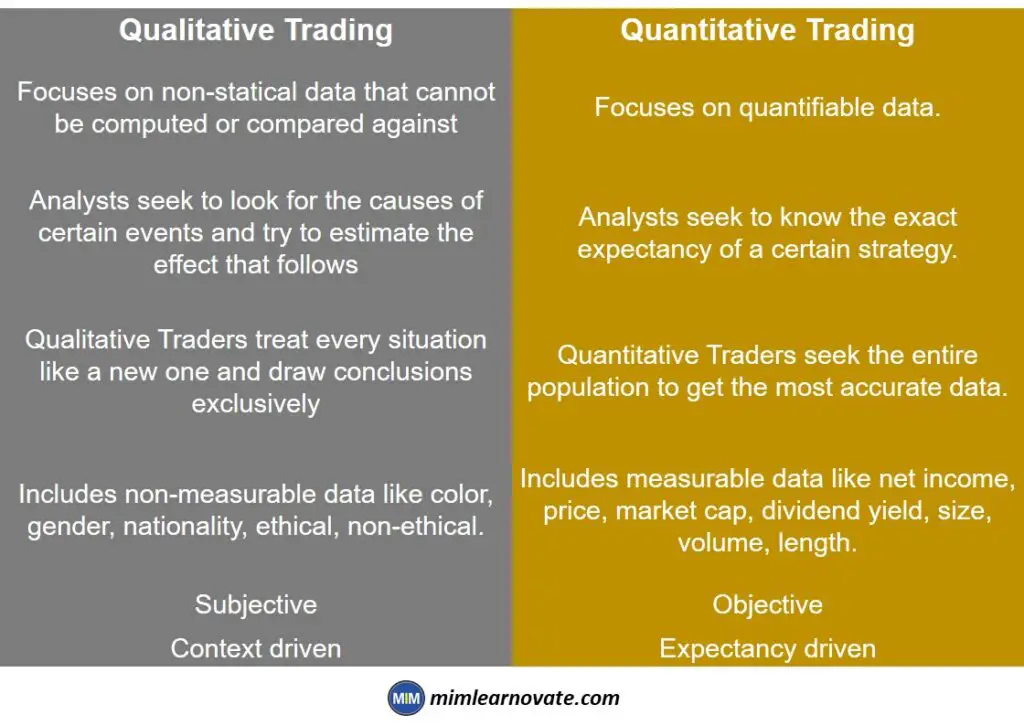
Qualitative Trading vs Quantitative Trading
| Qualitative Trading | Quantitative Trading |
| Focuses on non-statical data that cannot be computed or compared against | Focuses on quantifiable data. |
| Analysts seek to look for the causes of certain events and try to estimate the effect that follows | Analysts seek to know the exact expectancy of a certain strategy. |
| Qualitative Traders treat every situation like a new one and draw conclusions exclusively | Quantitative Traders seek the entire population to get the most accurate data. |
| Includes non-measurable data like color, gender, nationality, ethical, non-ethical. | Includes measurable data like net income, price, market cap, dividend yield, size, volume, length. |
| Subjective | Objective |
| Context driven | Expectancy driven |
Disadvantages of a qualitative process
1. Single-case analysis
A qualitative process and a quantitative process are most different when historical samples are taken into account. In other words, a “single-case analysis” is a term that is frequently used to describe a qualitative process.
Isolating a case has its own set of drawbacks and restrictions, with methodological rigour being the main one.
The analysis process has been put to the test numerous times and has been shown to give the researcher a wholistic conclusion, which is what is meant by methodological rigour. Theoretically, qualitative analysis is just opposite.
2. Vulnerable to biases
The main threat will then be biases when the analysis process is not fixed or “depends on the scenario.”
Survivorship bias, confirmation bias, and sunk-cost bias are just a few examples of the biases that traders frequently demonstrate. And until it’s finished, we won’t know if we’re making them unless someone else tells us. Even then, it would be considered to be biassed in hindsight.
In addition, it is considerably simpler for the trader to justify their position because there are no regulations to guard against bad choices.
For instance: “I’m just going to buy more because it’s getting cheaper and cheaper.” But when does the trader halt and declare, “I think it’s time for me to sell this loss.” Technically speaking, a qualitative trader is free to decide never to state that.
Disadvantages of a quantitative process
1. Context is ignored
All aspects of a quantitative trading process revolve around numbers and statistics. This process often yields a binary response: either yes or no. As a result, you will never understand the context of the occurrence.
How did the stock increase? Why did the stock decline in a gap?
This then results in the paradox of curve-fitting. Do you adjust your present strategy if you find something that is a strong buy signal? If you did, it would change the outcome of your approach and turn it into a completely other one.
2. You can’t know everything
When you automate, there are a few “unfortunate situations” you could find yourself in.
Sometimes, even the simplest programming errors—like placing a parenthesis incorrectly—can send you sliding towards a complete breakdown.
Although you may believe that putting stop losses in place has protected you, other things may have an impact on them. Every cause has a result, and since we are only human, we are unable to anticipate the unknown.
The computer is unable to safeguard you from this. AI could be able to do this, but even then, the best defense is still the instinctive human fight-or-flight response.
Types of quantitative trading strategies
Many individuals believe that quantitative trading is simply about utilising robots to counteract human emotions. However, there’s more to it than that.
Quantitative data can be used in a variety of ways to support a trader’s decision. Here are three ways that quantitative data might be useful for you:
Alternative data analysis
Not simply traditional data regarding a stock or a currency pair are available. The company’s performance is also influenced by measures outside of the charts, such as volume, price, market cap, net income, etc.
- The quantity of McDonald’s “check-ins” every month.
- How many trucks are departing the Ikea factory.
- Satellite pictures of the amount of vehicles parked in a Walmart lot.
Traders strive to stay one step ahead of their rivals as traditional trading strategies become more and more well-known. These are some of the innovative strategies they have developed as a result to gain that slight competitive advantage.
These are the quantitative data with significant entrance barriers that other traders do not have access to.
High-frequency trading (HFT)
High-frequency trading is a type of trading that is carried out at speeds that are impossible for humans.
This type of trading is characterised by a high volume of transactions and a low average profit per trade. As a result, the infrastructure required for achieving this is also relatively expensive.
types of high-frequency trading strategies
There are two main types of high-frequency strategies, further broken down as follows:
1- Machine learning
Machine learning techniques enable computers to perform specific tasks without being explicitly instructed. It occurs when the computer arranges the data and selects the crucial details to create its own thesis.
The key benefit is being able to assess massive amounts of data quickly, something that would have taken qualitative traders a very long time to do.
2- Arbitrage
When an asset is priced differently on two exchanges, arbitrage is the idea of buying the less expensive asset while shorting the more expensive one.
3- News releases
Being the first in a highly competitive market pays off. especially when significant news is announced.
Being in the highly competitive high-frequency trading industry has its drawbacks. The edge swiftly vanishes once the details of a specific strategy are made known to the general audience. That is why most HFT firms are highly secretive about what they do.


