“The adoption of Ethereum by the corporate world means it could eventually be bigger than its early stage rival.”, suggests CNBC.
It is now necessary to learn about the how does ethereum work, its key features, applications, and how it differs from Bitcoin.
Only Bitcoin currently surpasses Ethereum in terms of popularity, according to many. The Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA) was founded by some well-known companies, including Microsoft, Intel, and JPMorgan Chase, according to The Motley Fool.
What Is Ethereum?
The open-source operating system Ethereum provides support for smart contracts. It is a platform for distributed computing that facilitates the creation of decentralised digital applications (DApps) using blockchain technology.
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which is offered by Ethereum, is a decentralized virtual machine that can execute programs utilizing an international network of public nodes.

The largest decentralised application is Ethereum. It enables you to create decentralised applications and smart contracts without interruption from other parties. The developer can produce and publish next-generation distributed apps using Ethereum.
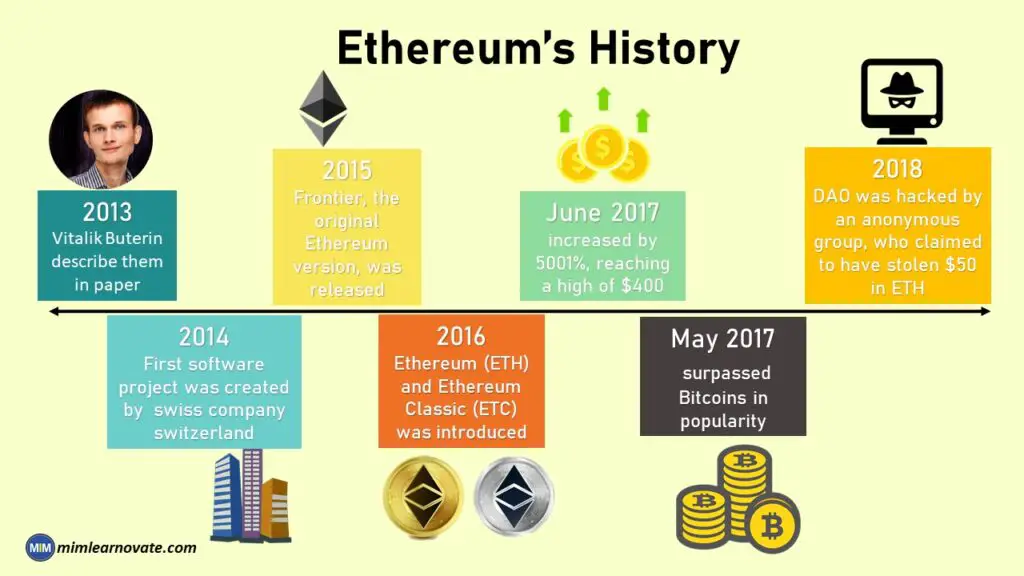
Ethereum’s History (2013- 2018)
2013: A developer named Vitalik Buterin was associated with Bitcoins, and he was the first to describe them in paper.
2014 : The first Ethereum software project was created in 2014 by the Swiss company.
2015 : Frontier, the original Ethereum version, was released in 2015.
2016 : On March 14, 2016, the Homestead protocol, which had been planned, underwent the second-largest version upgrade on the Ethereum network.
In May 2016, when the DAO raised a record-breaking $150 million through a crowd sale, Ethereum received the greatest media attention.
The network split into two major categories in July 2016: Ethereum (ETH) and Ethereum Classic (ETC).
June 2017: Since January 1, 2017, Ethereum has increased by 500%, reaching a high of $400.
May 2017: Ethereum eventually had surpassed Bitcoins in popularity.
June 2018: The DAO was hacked in June 2018 by an anonymous group, who claimed to have stolen $50 in ETH.
Need of Ethereum
One of the most common models for software applications is centralized systems. The operation of each unit and the information flow from a single center are directly controlled by this system. Individuals in this type of system depend on the central authority to send and receive information.
-Problem: Centralized System
There are problems with the centralized system, including:
- “Silo effect”
- Single point of failure and control
- It can easily become corrupt.
- Bottleneck in performance
-Solution: Decentralized Applications
Decentralized Applications are the ultimate solution for the problems that are faced using centralized systems. These applications communicate solely with a blockchain; they never respond to a centralized backend.
Decentralized apps or “DApp” are software, tools, or applications that operate on the decentralized Ethereum Blockchain.

What is Ether?
On the Ethereum blockchain, ether is a currency token. Exchanges for cryptocurrencies mention it as “ETH.”
You can use it to pay for computational services and transaction fees on the Ethereum network. Every time the contract is fulfilled in the Ethereum network, ether is paid.

Gas
On the Ethereum network, a user must pay a miner with ether through a middle token called “Gas” in order to complete a transaction.

It is a unit that lets you quantify the amount of computing needed to carry out a smart contract or other transaction.

The transaction fee in Ethereum is determined in ether and is expressed as
Ether = Tx Fees= Gas Limit * Gas Price
- The amount of gas used for the calculation is referred to as the “Gas Limit.”
- Gas price is equal to the amount of Ether that a user must pay.
Ethereum: Key Terms
Ether: Ethereum’s cryptocurrency is called ether.
Smart Contracts: Ethereum supports the creation and implementation of contracts of this kind.
Decentralized applications (Dapps): A Dapp, also known as a DAPP, App, or DApp, is a type of decentralised application. You may build consolidated applications—also known as decentralised applications—using Ethereum.
Decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs): You can construct decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs) using Ethereum to facilitate democratic decision-making.
Ethereum Virtual Machine: Ethereum gives you access to the architecture and software, as well as the underlying technology, that allows you to engage with smart contracts
Smart Property: On the Ethereum blockchain, decentralised applications can be accessed using the Ethereum wallet. It enables you to store and protect ether and other Ethereum-based cryptoassets.
Solidity: The smart contract language used in Ethereum is called Solidity. It is a general-purpose language created to function in the EVM environment. You can make arbitrary computations with the aid of solidity. But its main functions are to send and receive digital tokens and to store states.
Transactions: A transaction is a communication delivered from one account to another, which could be the same account or an empty one. It is possible for it to include binary data, or “ether.”
Currency Issuance: The central bank of a nation oversees and manages it primarily. It is additionally known as a monetary authority.
Smart Contracts vs Traditional Contracts
Here is the difference between Smart Contracts and Traditional Contracts:
| Smart Contracts | Traditional Contracts | |
| Execution | Agreement is coded in a program. | Agreement is executed by a third party. |
| Specification | Code | Human language |
| Identity | Digital Signatures | Wet Signatures |
| Duration | 1-3 Days | Minutes |
| Remittance | Automatic | Manual |
| Cost | Cheap | Expensive |
| Presence | Virtual | Physical |
| Data | Decentralized on blockchain | Centralized |
| Third party | Financial companies act as third party. | No third party involved |
| Privacy | Data Privacy risks | No Data Privacy risks |
| Escrow | Necessary | Not Necessary |
How do Smart Contracts work?
A computer program that runs automatically is a smart contract. It is a protocol for transactions that enables the trading of money and assets among blockchain users. Additionally, it enables users to carry out tasks like voting independently. It functions as a virtual third-party software agent that can autonomously carry out and enforce the terms and obligations of the contract.
Example of Smart Contracts
Suppose John hired Anna to create the website for his business and paid her $500 for the job. The smart contract’s agreement is built by the developers using the Ethereum programming language.
All of the prerequisites (conditions) for developing the website are present in the smart contract. The written code is uploaded and deployed on the Ethereum Virtual Machine after completion (EVM).
A smart contract can be executed using EVM, a runtime compiler. Every member of the network owns a copy of the contract once the code is installed on the EVM.
Each node on the Ethereum network will assess and confirm whether Anna’s work has been completed in accordance with the coding criteria when she submits it to the Ethereum network for evaluation.
The $500 contract will self-execute after the outcome has been accepted and verified, and Anna will be paid in ether. Anna will be given $500 in ether, and John’s account will be promptly debited.
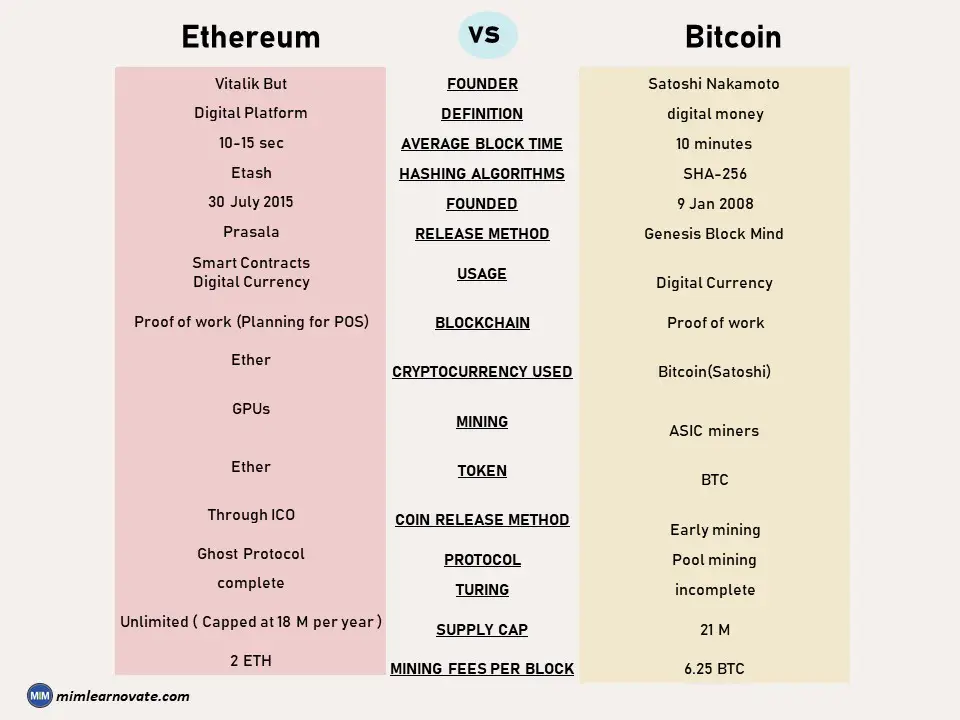
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin
Ethereum | Bitcoin | |
| Founder | Vitalik But | Satoshi Nakamoto |
| Definition | Digital Platform | digital money |
| Average Block time | 10-15 sec | 10 minutes |
| Hashing algorithms | Etash | SHA-256 |
| Founded | 30 July 2015 | 9 Jan 2008 |
| Release Method | Prasala | Genesis Block Mind |
| Usage | Smart Contracts Digital Currency | Digital Currency |
| Blockchain | Proof of work (Planning for POS) | Proof of work |
| Cryptocurrency Used | Ether | Bitcoin(Satoshi) |
| Mining | GPUs | ASIC miners |
| Token | Ether | BTC |
| Coin Release Method | Through ICO | Early mining |
| Protocol | Ghost Protocol | Pool mining |
| Turing | complete | incomplete |
| Supply Cap | Unlimited ( Capped at 18 M per year ) | 21 M |
| Mining Fees per block | 2 ETH | 6.25 BTC |
Benefits of Ethereum
These are some benefits of Ethereum:
- Enables you to upload and request the execution of programs.
- Create virtual companies.
- You can create decentralized programs that are fault-tolerant and extremely secure using Ethereum.
- DDOS resistant and 100% uptime.
- Aids in the creation of decentralized apps.
- You can use a tradable token you develop using Ethereum as a virtual share or new currency.
- Continuous and permanent data storage.

Drawbacks of Ethereum
- The cost of blockchain storage is high.
- Due to the lack of a centralized authority to validate user identities, some applications require user identity verification.
- Swarm Decentralization involves a trade-off because scaling is a problem. Private block chains will probably become more common.
- You cannot utilize the Ethereum Virtual Machine for complex computations due to its slowness.
- It is difficult to fix faults or update apps because each peer in the network must upgrade their node software.
- There is a trade-off between decentralization and private block chains since swarm scalability is a problem.
Application of Ethereum
Banking:
Because of its decentralized approach and difficulty for hackers to get illegal access, Ethereum is being rapidly embraced in banking systems.
Banks are adopting Ethereum as a gateway for sending money overseas and making payments because it also permits transactions on an Ethereum-based network.
Prediction market:
Another fantastic application of an Ethereum Smart Contract is the prediction market. Ethereum is used for this by platforms like Gnosis and Augur.

Digital Identity Management:
The main problems of identity theft and data monopoly can be resolved by using smart contracts to handle digital identities.
Agreements:
Agreements can be implemented and maintained without change using Ethereum smart contracts. Ethereum can therefore be used as a technology for creating smart contracts and for digitally storing the agreements and the transactions based on them in an industry that has dispersed participants, is prone to disputes, and needs the presence of digital contract.
Shipping:
Implementing Ethereum in the shipping industry makes it easier to trace cargo and protects against misplaced or fake items.
The provenance and tracking framework needed for any asset in a normal supply chain is provided by Ethereum.
FAQs about Ethereum
1- How Can I Buy Ethereum?
To purchase and sell ether, investors can use one of the many cryptocurrency exchange websites. Dedicated cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase, Kraken, Gemini, Binance, and brokerages like Robinhood support Ethereum.
2- Can Ethereum Be Exchanged for Cash?
Yes. Online exchanges like Coinbase, Kraken, and Gemini are available to investors who own the cryptocurrency ETH for this operation. Simply create an account on the exchange, link a bank account, and transfer ETH from an Ethereum wallet to the exchange account.
Place a sell order for ETH on the exchange. Once sold, transfer the US dollar earnings to the associated bank account.
3- How Does Ethereum Make Money?
Ethereum is not a centralized business that generates revenue. The Ethereum network pays validators who take part with ETH for their contributions.
4- Is Ethereum a Good Investment?
The answer to that relies on your financial goals, objectives, and risk tolerance, just like with any investment. Capital may be at risk due to the volatility of the ETH cryptocurrency. Nevertheless, it i
s unquestionably worth looking into as an investment because the different current and future creative technologies that utilize Ethereum may come to play a bigger part in our society.
5-Is Ethereum a Cryptocurrency?
Ether, sometimes known as ETH, is a native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum platform. In addition to cryptocurrencies, a wide variety of decentralised apps (DApps) are supported by the blockchain technology platform Ethereum.
Ethereum is the name given to the ETH token, although this does not change the fact that Ethereum is a blockchain-powered platform, and ether is its cryptocurrency.
6-What is Ethereum used for?
Ether is primarily used for four things: trading as a digital currency on exchanges, holding as an investment, making purchases of goods and services, and paying transaction fees on the Ethereum network.
7- Who owns Ethereum?
Ethereum is a blockchain platform for decentralised financial applications that was co-founded by Vitalik Buterin. When Ether, the native cryptocurrency of Ethereum, first surpassed $3,000 per coin in May 2021, he became the youngest crypto billionaire in history. He was 27 years old at the time.
Read More:



