It can be easy to become confused when first learning about components of computer architecture. There are so many different components, manufacturers, standards and features that it’s no wonder new users can feel a little lost. However, this article will explain everything you need to know about computer motherboards as well as related computer components such as the BIOS, radiators, cables and ports.

This blog post focuses on motherboards and the other primary internal computer components in general. We cover the essentials of each component along with more advanced details only relevant to those who want to know more. If you’re looking for information on kinds of computer components continue reading for an in-depth analysis of popular components.
The components of a computer are the parts that are required for it to function. These include the display, keyboard, mouse, central processing unit, memory and storage devices. A computer is a machine that processes information as part of a system. The motherboard, CPU, peripheral devices, and storage devices are the main components of a computer.
Input Devices
Through input units or devices like a keyboard, joystick, etc., computers can receive commands in the form of numbers, alphabets, images, etc. and respond accordingly. The responses are then output in a language that humans understand or that we have programmed the computer with. These inputs are then analyzed and converted to computer language.
1- Keyboard
The most frequent and well-liked input method for entering data into computers is the keyboard. Although there are some extra keys for performing other operations, the keyboard layout is similar to that of a typical typewriter.
Keyboards typically have 84 or 101 or 102 keys, although lately keyboards with 104 or 108 keys are also available for use with Windows and the Internet.

The following is a list of the keyboard’s keys:
▶ Typing Keys
These keys contain digit keys (09), which normally have the same layout as typewriters, and letter keys (A–Z).
▶ Numeric Keypad
It is utilized for cursor movement or entering numerical data. It typically consists of a set of 17 keys that are arranged in a manner consistent with that of the majority of adding machines and calculators.
▶ Function Keys
The keyboard has twelve function keys, which are located at the top of the keyboard in a row. Each function key has a distinct meaning and serves a certain function.
▶ Control keys
These keys allow you to control the screen and cursor. It has four arrow keys for direction. Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control (Ctrl), Alternate (Alt), and Escape are additional control keys (Esc).
▶ Special Purpose Keys
In addition, the keyboard has some keys with specific functions, including Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space Bar, Tab, and Print Screen.
Mouse
The cursor or pointer is moved across the screen using the mouse, a portable input device. It often has a scroll wheel between the left and right buttons and is made to be used on a flat surface. A touchpad that doubles as a mouse is included with laptop computers. It lets you control the movement of cursor or pointer by moving your finger over the touchpad. Some mouse have built-in capabilities like additional buttons that can be used to execute other buttons.

Douglas C. Engelbart created the mouse in 1963. A roller ball was incorporated underneath early mice as a movement sensor. Modern mice are equipped with optical technology, which uses a visible or invisible light beam to control cursor movement. Depending on the type of computer and mouse, a mouse is linked to a computer by a different port.
Common types of the mouse includes:
1- Trackball Mouse
It is a stationary input device that moves the pointer or cursor on the screen using a ball mechanism. To move the pointer on the screen, just roll the ball, which is partially placed in the device, with your finger, thumb, or palm. The gadget features a sensor that can identify ball rotation. You don’t need to move it off the operational surface; it stays put. As you don’t need to move it like a mouse, it is the perfect device if you have a little desk.

2- Mechanical Mouse
Its tracking system consists of a ball and multiple rollers. It is a mouse with a cord. High performance can be achieved by using a mechanical mouse. The disadvantage is that they frequently get dust into the mechanics, necessitating routine cleaning.

3- Optical mouse
An optical mouse tracks its movement using optical circuitry. It requires less upkeep and is more dependable than a mechanical mouse. However, the operating surface has an impact on how well it performs. For best performance, a simple, non-glossy mouse mat should be utilized. The optical identification system may experience difficulties due to the surface’s roughness, and tracking difficulties may result from the glossy surface’s inaccurate light reflection.

4- Cordless or Wireless Mouse:
As the name implies, this sort of mouse has no cables and instead moves the cursor using wireless technologies like IrDA (infrared) or radio (Bluetooth or Wi-Fi). It is utilized to enhance the mouse-using experience. It uses batteries for its power supply.

Joystick
A joystick is another pointing device used to change the location of the pointer on a monitor screen. It is a stick with spherical balls at both the lower and upper ends. The lower spherical ball moves in a socket. You may rotate the joystick in all four directions.
The joystick performs comparable duties to a mouse. It is primarily utilised when playing video games and performing computer-aided design (CAD).

Scanner
The images and text pages serve as input for the scanner. The image or document is scanned. The scanned picture or document then converted into a digital format or file and is displayed on the screen as an output. In order to transform photos into digital ones, it employs optical character recognition techniques. The following are some examples of common scanner types:
Various Scanner Types are :
1- Flatbed scanner
It has a moving optical CIS or CCD array and a glass window. The image is first placed on the glass pane once the light has illuminated it. The document is scanned by the light as it passes across the glass pane, creating a digital replica of the original. When scanning transparent slides, you will want a transparency adaptor.

2- Handheld Scanner
It is a tiny manual scanning tool that is rolled over a flat image to be scanned while being held in the hand. The disadvantage of utilising this gadget is that the hand needs to remain stable during scanning in order to prevent image distortion. The barcode scanner you’ve probably seen in stores is one of the more often utilised handheld scanners.

3- Sheetfed Scanner
The document is placed into the scanner’s given slot while using this one. The sheet-feeder, scanning module, and calibration sheet are the scanner’s major parts. In this scanner, the light is stationary. The document instead passes through the scanner. It is best suited for scanning documents with a single page, not bulky items like books, magazines, etc.

4- Drum Scanner
A photomultiplier tube (PMT) is used in drum scanners to scan images. It lacks a charge-coupled component like a flatbed scanner would. The photomultiplier tube is incredibly light-sensitive. The image is mounted on a glass tube, and as light passes over it, a reflection of the image is created. This reflection is picked up by the PMT and processed. These scanners can handle detailed scans thanks to their high resolution.

5- Photo Scanner
It is intended to scan pictures. For scanning images, it must have a high resolution and colour depth. Old photograph cleaning and restoration software is built right into some photo scanners.

Bar Code Reader
A barcode reader is a device for reading bar-coded information (data in the form of light and dark lines). Bar coded data is generally used in labelling goods, numbering the books, etc. It may be a handheld scanner or may be embedded in a stationary scanner.
A bar code reader scans a bar code image, transforms it into an alphanumeric value, and then feeds that value to the computer to which it is attached.

Touchpad
It typically serves as a mouse replacement in laptops. You can use your finger to move or manage the cursor on the screen. It also has two buttons for right and left clicks, just like a mouse. You can use the touchpad to carry out any mouse-related actions, including selecting an item on the screen, copying, pasting, deleting, opening a file or folder, and more.

Microphone
The sound is entered into the computer through the microphone. It captures the sound vibrations and either transfers them to a recording device or turns them into audio signals. The computer transforms the audio signals into digital data and stores it. The microphone also enables the user to telecommunicate with others. Additionally, it is used for video conferencing with webcams and to provide sound to presentations.

Studio microphone and pop shield on mic in the empty recording studio with copy space. Performance and show in the music business equipment.
Output Devices
The output is what we get back from the instruction we gave the computer through the input device. The monitor is the device that is utilized the most since commands are entered via the keyboard, and the outcome is shown on the monitor after processing.
1- Monitor
The earliest televisions and monitors shared the same cathode ray tube and fluorescent screen technology. The Uniscope 300 device, which had a built-in CRT display, was the first to use this technology for computer monitors in 1965. A beam of light from a CRT display illuminates a string of dots on the screen’s active area. The greatest resolution as a result was 1600 by 1200 pixels. In 2007, sales of LCD (liquid crystal display) displays surpassed those of CRT (cathode ray tube) monitors. Monitors today include flat display technology. Plasma, or tiny charged gas bubbles, illuminates the screen of plasma monitors, which are brighter than CRT and LCD displays.

The most important output devices for a computer are its monitors. The computer would be incomplete without it. The computer’s monitor is a flexible component for the visual display of all kinds of data.
The monitor is made to show both graphical and symbolic data. On its screen, it displays all the facts and information in soft copy. It serves as a conduit between the user and the CPU.
To show the data, a cable is attached to a video adapter installed on the computer’s motherboard. Anyone can use the display to examine files, pictures, videos, text, graphics, and tables in real time.
On the monitor, you can view files, pictures, videos, text, graphics, and tables in real time. They are created with more frequency in thinner widths and using cutting-edge technologies like LED, plasma, or liquid crystal.
The dimensions of this output device range from 15, 17, 19, and 21 inches across. Laptop monitor screens, however, are significantly more delicate and compact.
Basically, there are 5 different types of monitors.
1- CRT Monitors (Cathode Ray Tube)2- LCD Monitors (Liquid Crystal Display)3- LED Monitors (Light Emitting Diode)
4- OLED Monitors (Organic Light Emitting Diode)2- Printer
Printing information on paper is done using a printer, which is an output device. A printer is a computer’s electrical external output device used to produce tangible copies of digital information on paper. Since turning data from soft copy to hard copy on a computer is the primary function of printers.
Depending on the page size, the printer outputs tiny or large versions of the files that are saved in a computer (data can be in text form). In offices, homes, PPT, and commercial settings, printers are used to print signage and business papers.
DPI (dots per inch) resolution is a unit used to measure the resolution or clarity of images generated by printers. The higher quality can be printed and seen more clearly with a printer that has more dots per square inch.
The printer is typically only connected wirelessly over wifi or by a data cord to a computer. Many digital printers today come equipped with the newest wireless technologies, including Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and cloud storage. The task of printing is made simpler as a result.
Ctrl + P is the shortcut command to print the documents quickly.
There are two different kinds of printers
1- Impact Printers
2- Non-Impact Printers
Impact Printers
Characters are printed on the ribbon in impact printers before being pressed against the paper.
Impact printers have the following characteristics:
⫸ Very low consumable costs
⫸ Very noisy
⫸ due to its low cost, it is useful for printing in bulk
⫸To create an image, physical contact is made with the paper.
1- Dot Matrix Printer (DMP)
Dot Matrix Printers are among the most widely used printers on the market. These printers are well-liked due to how simple and inexpensive they are to use.
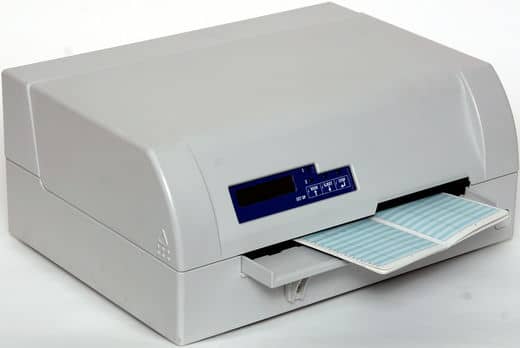
The head of the printer is made up of a matrix of pins with sizes of (5*7, 7*9, 9*7 or 9*9), and each character is produced as a pattern of dots. For this reason, the printer is also known as a dot matrix printer.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Inexpensive | Widely Used |
| Slow Speed | Poor Quality |
Non-impact Printers
Characters are printed using non-impact printers without the need of ribbon. These printers are also known as page printers since they print an entire page at once.
Non-impact printer characteristics:
⫸ Faster than impact printers
⫸They are not noisy
⫸ High quality
⫸ Supports many fonts and different character size
There are two types of non-impact printer:
1- Laser Printer
These are non-impact page printers. The dots required to create the characters that will be printed on a page are created using laser lights.

| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Very high speed | Expensive |
| Good graphics quality | Cannot print large copies of a document at once |
| Supports many fonts and different character size | |
| Very high quality output |
2- Inkjet Printers
Non-impact character printers that use inkjet technology are relatively new. They use little drops of ink to print characters onto paper. Inkjet printers produce high quality output with presentable features.

Due to the absence of hammering, they are quieter and offer a variety of printing options. Printing in color is also an option. Multiple copies of the same print job can be produced by some inkjet printer types.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High quality printing | Costly due to the high cost per page |
| More reliable | Slower than a laser printer |
4- Plotter
A plotter is an output device that prints graphics in many different color formats with high-quality images. Although it is similar to a printer, it offers more sophisticated features.

The plotter enables us to print huge maps, architectural drawings, large-format printing, images, 3D postcards, advertising signs, charts, and various designs of the interior structure of building machinery.
The plotter can print on cardboard, fabric, film, and other synthetic materials, but the printer can only print on paper. You may print on T-shirts, backpacks, other lightweight apparel, round things like cups, and even some unusual printing models.
Because they are faster, more accurate, and have high-resolution graphics, plotters are different from printers. Plotters are therefore employed in engineering applications by engineers and architects where accuracy is essential.
According to the instructions provided by the computer user, printers create the images. In this instance, multicolor plotters are created using various coloured pens.
On big sheets of paper, drawing graphs of excellent quality are produced using a plotter. In engineering, building construction, city planning, map-making, etc., it is primarily employed. A plotter is significantly more expensive to purchase than a printer.
5- Speaker
A hardware output device known as a speaker that is connected to a computer to produce audio. A sound card is a piece of hardware that comes pre-installed with computers and creates the sound that is played through the speakers.
There is no technical term for “speaker.” The device’s official term is “dynamic head.” These days, this Speaker can be found on a variety of gadgets, including TVs, radios, phones, children’s toys, and more.

To create the sound coming from a computer speaker, the audio signal is routed through the sound card of the computer. At the top of the keyboard on many LAPTOPs is an embedded speaker.
Internal Speaker refers to the speaker that is incorporated into the motherboard. When amplifying computer sound, an external speaker may be required in addition to the built-in one.
6- Headphone
With headphones, you can listen to any sound signals that are being communicated by an electronic device. These are hardware units that create audio in private after being wirelessly connected to smartphones or PCs.
When in a crowd, the main benefit of utilizing headphones or earbuds is to listen to the audio in solitude without disturbing others. The sound card (or any other connected device) provides audio input, which the headphone turns into audio output in the form of wave sound.

In today’s digital era, many headphones and earbuds are introduced with cutting-edge technology and superior sound technology. These headphones are compatible with any audio equipment that has a 3.5 mm jack port.
Several benefits of headphones over speakers include:
⫸ High-quality audio
⫸ Purchasing headphones is far less expensive than purchasing a dedicated speaker system
⫸ Separation from outside audio signals
Motherboard
A motherboard is a circuit board that serves as a communication channel for all of a computer’s parts and serves to keep everything connected. In order for them to work, the input and output devices must be plugged into the motherboard.
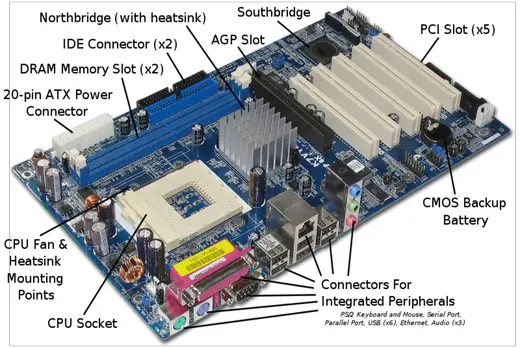
There are many components of motherboard but some important are written there:
• CPU
• North bridge, south bridge
• RAM and ROM
• Parallel port and Serial port
• Buses
• Network card
• Logic gate
• Data cable & Electrical cable
• System clock
• Sound card & Graphic card
• Transistor, Capacitor
• Power supply
• USB Port
• CPU Cooler
• ATX Power supply
CPU (Central Processing Chip)
The microprocessor chip, usually referred to as the CPU, is the primary chip found in computers. The CPU is mounted on a printed circuit board called the main board or mother board.
Since it serves as the main processing unit and controls all actions, the CPU is referred to as the computer’s brain. It has three components that support the CPU’s efficient operation and communicates with every other part of the computer. The components of the CPU are:

The data entered through the input devices is saved in the CPU’s memory before being sent to the other components. In a similar manner, when the output is ready, it is saved in the memory prior to the user seeing the result.
Control Unit
This part of the computer regulates how it works. When data is entered, it gathers it, sends it for processing, waits for the results, and then gives the user what they need. The control unit is therefore referred to as the center of all processing actions that occur in a computer since it receives instructions, decodes them, signals execution, and receives the output.
Arithmetic Logic Unit
Mathematical calculations, arithmetic operations, data comparison, and decision-making are all done in this unit. It has circuits designed for multiplication, division, addition, and other calculations.
Logical Gates
Any computer system’s fundamental building blocks are logic gates. It is an electronic circuit with a single output and one or more inputs. The relationship between the input and the output is based on a certain\slogic. Logic gates are given names like AND gate, OR gate, NOT gate, etc. based on this.
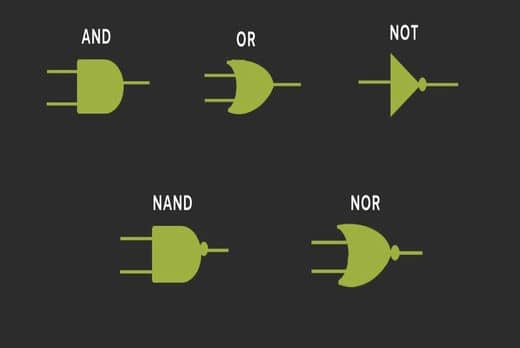
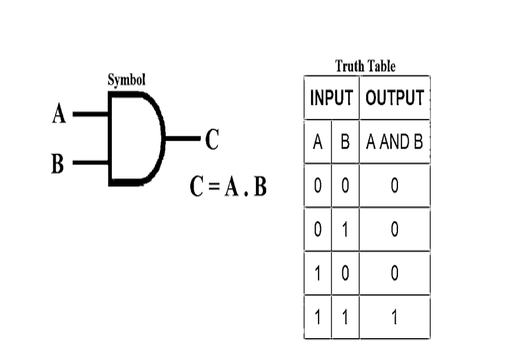
1- AND Gate
Figure depicts a circuit that executes an AND operation. It has one output and n inputs (n >= 2).
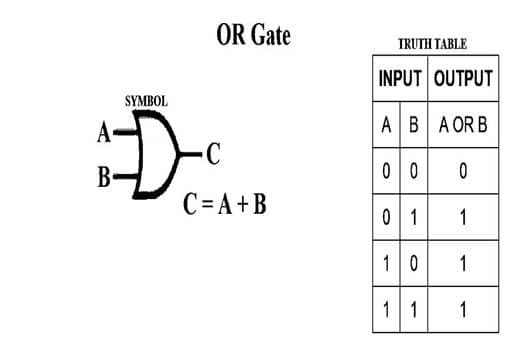
2- OR Gate
In the illustration, a circuit that performs an OR operation is depicted. It has one output and n inputs (n >= 2).
NAND Gate
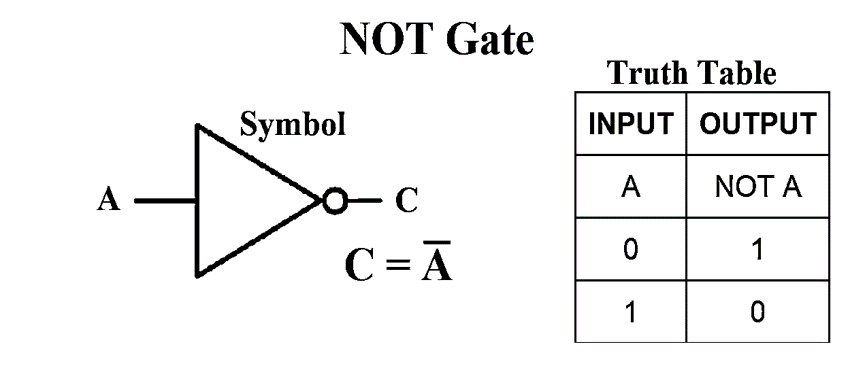
3- NOT Gate
NOT gate is also known as Inverter. It has one input and one output .
Cache
Cache memory is also referred to as CPU (central processing unit) memory since it is either built right into the CPU chip or placed on a different chip with a different bus link from the CPU.
It is very fast similar to RAM.

Information, data, and programs that are often needed by the CPU are temporarily stored in cache memory. The CPU will automatically access cache memory when data is needed in order to access data more quickly. This is due to slower server RAM and its greater distance from the CPU.
When a program is running and CPU needs to read data. It first checks whether the data is in cache memory. If the data is not there, then the CPU loads the data from RAM to registers and also loads a copy to cache.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| faster than main memory | limited capacity |
| consumes less access time as compared to main memory | very expensive |
| stores data for temporary use |
Data or instructions that the CPU is likely to need in the near future are kept in cache memory. Caching is used to improve read performance since it avoids the CPU from having to wait.
Network Card
The network card is the part of the computer that allows you to connect to a network. This is usually a simple plug-in card that connects to your motherboard. Network cards allow you to connect to a network using either an Ethernet cable or a wireless connection. The cards are controlled by the operating system on the computer.
Bluetooth
The Bluetooth chip is a small circuit that allows the computer to wirelessly connect to other devices. Depending on the motherboard, it may be possible to connect to Bluetooth speakers, headphones and other devices. The devices will also need to have a compatible Bluetooth chip. There are different versions of Bluetooth chips. The most recent versions generally have faster transmission speeds.

Sound Card
The sound card is the part of the computer that controls audio. This can be sound from a game, music from a streaming service or an online video. The sound card is separate from the speakers. You should connect the speakers to the sound card with an audio cable. The sound card has an integrated circuit that can process audio data. It also has ports for connecting speakers and an audio cable.

Graphic Card
The graphic card is a circuit board inside the computer that processes images. Computer images are made up of millions of tiny pixels. You can think of the graphic card as a kind of super-powerful computer chip that makes it easier to process images. The graphic card is also connected to the motherboard. This allows it to connect to other components in the computer, such as the CPU and RAM. Depending on the type of graphic card, the computer can be used for things like playing computer games, editing photos or creating graphics.

Bus
A bus is a data communication pathway between computer components, or between computers, consisting of a set of parallel conductors that may be connected by intermediate devices such as repeaters or hubs. It is an interconnection between computer components that is used to transfer data between them. The bus is the main communication pathway between the computer’s functional units. It is the central channel for information exchange between the computer’s central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output devices, and other functions. The bus is where information is transferred between the computer’s various functional units. I

A bus is a subsystem that links computer parts and allows data to be transferred between them. For instance, a motherboard and computer internals are connected by an internal bus. Bits are moved both internally and externally using computer buses. Internal transfers include those between the processor and the cache as well as the CPU and the memory. And by external transfer, we mean that the bus sends data out to printers and other external devices from memory.
1- Data bus
A data bus is a means of transferring data bits between the CPU and memory as well as between memory and other computer internals like cache and registers.
The CPU sends the address of the memory location or the input/output port that will be immediately accessed across the address bus. It is a unidirectional bus, meaning that the address can only be sent from the CPU to the needed port or location.
The CPU determines the address of the necessary data and transmits it on the data bus for the execution of the necessary operation, whether it is a read or write operation. The number of address bus lines in a system determines how many memory locations can be accessed at once.
2- Address bus
Address bits are transferred to the memory using the address bus. Every memory region in RAM or memory has an address. Memory addresses are assigned by the CPU, and these addresses are sent through the address bus.
An address bus of n lines can be addressed at the most 2n locations directly. As a result, a 16-bit address bus can access 64 K Bytes or 2 16-bits of memory.
Data and instructions are transported in both directions from the CPU to memory and peripheral devices using a data bus. It is a bidirectional bus as a result. Due to the fact that every programme instruction and every byte of data must pass via the bus at some point, it is one of the most crucial components of the connections to the CPU.
3- Control bus
Control bits are transferred from control units to other computer components via the control bus. Control refers to, for instance, deciding whether to write or read data from a memory device, erase any value from a memory device, increase a value, or read data from an input device. The control bus is used to transport these decision-making pieces.
The data bus’s size is expressed in bits. The size of the data bus greatly affects the computer architecture because it determines and controls key elements of that architecture, such as word size and data quantum, among others.
A microprocessor is typically referred to as an n-bit processor. So, as the CPU developed, the data bus expanded in size. When opposed to an 8-bit processor, which can only transfer one byte each bus cycle, a 64-bit data bus can transport eight bytes in each bus cycle.
Multiple individual lines conveying synchronized signals for control are found on a control bus. Numerous peripherals were linked to the CPU. Memory reads, memory writes, I/O reads, I/O writes, and other common signals are sent from the CPU to devices via the control bus.
Signals are designed with the microprocessor’s design philosophy and the needs of the numerous devices attached to the CPU in mind. As a result, many microprocessor types have various control signals.
Capacitors, Transistors
The motherboard also contains capacitors, transistors which are other important parts of the motherboard. Capacitors are small containers filled with electric charge. These are used to store energy. They are connected to the other parts of the circuit board through transistors.
RAM
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a type of computer storage that holds information while the computer is on. This means that any data you save to RAM will be deleted when the computer is shut down or restarted.
RAM is used to store the programs you’re running, as well as any data that is in use. For example, you might have a spreadsheet open on your computer that stores data. The computer will load this data into RAM so that the data can be easily accessed and modified. If you open a document that’s stored in a large file on your computer’s hard drive, the computer will load only that document into RAM. This is because you can only view one document at a time.

ROM
On the other hand, ROM is an electrically erasable programmable read-only memory that retains information even when the computer is shut down. In other words, ROM will not be erased even if you shut down your computer.

BIOS chip
BIOS stands for “Basic Input / Output System.” This BIOS chip is responsible for controlling the most fundamental components of your computer, including the loading of the operating system. The BIOS chip allows you to set up your computer’s hardware before you even start the operating system. This BIOS chip is usually located inside the computer’s motherboard and can be accessed through a special set of computer instructions called the “BIOS setup” menu. The BIOS setup menu will allow you to change the settings of your computer’s hardware.

CMOS Chip
CMOS stands for “Computer Management Open-Source.” Unlike the BIOS chip, there is no standard CMOS chip. Instead, CMOS chips are designed specifically for the computer motherboard they will be installed in.
A CMOS chip is a type of integrated circuit that is used to store information in the same way that a computer’s hard drive stores information. You can think of the CMOS chip as a “copy” of your computer’s BIOS settings. The CMOS chip is programmed by the BIOS chip, so any changes you make to your computer’s BIOS settings will also be saved to the CMOS chip.
North Bridge / South Bridge
These act as communication channels between the CPU and any attached peripherals. These facilitate communication between the CPU and the I/O ports and memory.
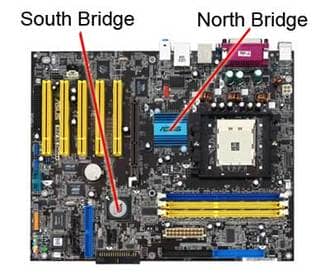
The Northbridge is in charge of tasks that call for the highest performance because it is directly connected to the CPU via the front-side bus (FSB). It controls communication between the CPU and other motherboard components. Typically, a southbridge is linked with a northbridge.
Southbridge can control PCI Bus, ISA or LPC Bridge, SPI Bus, SMBus, DMA Controller, Mass Storage, Real-time Clock, BIOS, and Audio. It also manages a computer’s I/O Ports.
Serial Port
In computer terms, a port is the physical connection between the computer and a device. The serial port was a standard computer port that was used before USB ports were invented. The serial port transfers data one bit at a time. The serial port is now obsolete, and most computers will no longer have a serial port. However, there are still a few devices that use the serial port. This includes some types of computer modems and older printers.

Parallel Port
The parallel port transfers data all at once. Parallel port is still used in many printers. However, it is now commonly used to connect computers to other devices such as scanners or thermal printers.

USB port
Perhaps the most common port you will see on a computer motherboard is the USB port. USB stands for “Universal Serial Bus.” This port allows you to connect a variety of different devices to your computer, such as printers, scanners, external hard drives and flash drives. The USB port transfers data between your computer and the connected device. Every USB port has a standard design that is used for all types of USB devices. This means that you can plug in a device that uses a specific type of USB port into any computer that has one of the standard USB ports. Although USB ports are common on computer motherboards, they are also found on many other types of devices.

SATA port
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, often known as Serial ATA or SATA. Mass storage devices, including as hard drives and optical discs, can connect with the motherboard utilizing a high-speed serial cable over two pairs of wires.
- SATA data cable
- Power cable

SATA (Serial Advanced Technology) cables are connectors that connect SSDs, HDDs, and optical drives to the motherboard in modern PCs. Your computer’s motherboard contains SATA ports, which number between four and eight (usually an even number). Typically, these ports resemble L-shaped connectors.


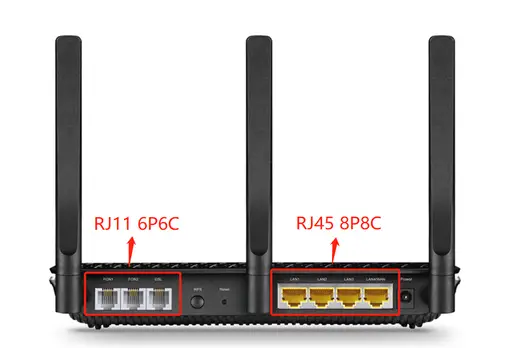
RJ45 / RJ 11 port
RJ stands for Registered Jack.
RJ45
- 8 Position
- 8 Pin/Conductor (4/8 options)
- Mainly used in network wiring.
- 6mm * 11mm
RJ45 connectors can handle speeds of up to 10Gbps over Ethernet, but only if the surrounding hardware, such as network cables, can handle that speed.
RJ11 connects to telephone units while RJ45 is typically used with Ethernet cables. RJ45 has eight wires inside, whereas RJ11 only has four wires. RJ45 is larger than RJ11 in size.
RJ11
- 6 Position
- 4 Pin/Conductor (2/4/6 options)
- Used for telephone, and (ADSL/VDSL) modem, etc.
- 6mm * 9.5mm
RJ11 connectors have a 100+ Mbps bandwidth capacity.


HDMI Port
Digital video and audio information are transferred using HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) cables between electronic devices like computers and HDTVs.
HDMI connectors have 19 pins
The HDMI ports are found either on the video card or the motherboard on the back of the computer.

Power Supply
The power supply is an electromechanical device that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). In other words, it changes the type of power that comes into the computer from the wall. This type of power is then used to power the different computer components, such as the computer motherboard, hard drive and power supply.
The power supply is connected to the computer’s motherboard by a special connector known as a “DC connector.” This DC connector is usually located on the back of the computer. The power supply is connected to the wall with an electrical cable. The more components your computer has, the more power it will need. This is why some computer motherboards will have multiple DC connectors. These DC connectors are used to power the computer’s components.
The power supply is an important computer component that can easily be damaged if not properly maintained. If you notice that your computer is not running as efficiently as it once did, or if it has started to make strange noises, then you may need to replace your power supply.

Data Cable
A data cable is made specifically for transferring data. In general, they transfer electronic data back and forth between sources and destinations. They frequently build connections between many locations all over a network on computer and telecommunications platforms.
Data cables are employed in a range of settings and circumstances due to their adaptability. To make sure that a computer runs as smoothly and effectively as possible, they could link the hardware components inside of it so that they are constantly in contact with one another. They can also carry signals between different computer networks, ensuring that information is shared instantly, consistently, and of course securely.

However, the most frequent occurrence of a data connection in our daily life is when we need to connect and transmit data between peripheral devices.
There are many different types of data cable, including the following:
▶Ethernet Cable – This is used to connect a computer to a network or another computer.
▶Firewire Cable – This cable is used to transfer data in and out of a computer.
▶HDMI Cable – This cable is used to connect a computer to a monitor or television.
▶USB Cable – This cable is used to transfer data from one device to another.
▶USB-C Cable – This cable is used to transfer data from one device to another. It can also be used to charge devices.
CPU Cooler
A CPU cooler is a device made to remove heat from the system CPU and other enclosure components. Lowering CPU temperatures with a CPU cooler enhances system performance and stability. However, including a cooling device may raise the system’s overall noise level.

LIQUID CPU COOLING
A different kind of CPU cooling is known as liquid cooling, in which a liquid circulates via tiny pipes in a heat sink to transfer heat from the CPU to a special radiator on the system enclosure or case before being released into the outside air. To continue the process, the cooled liquid returns via the system to the CPU.
AIR CPU COOLERS
A heat sink, which is a component used to reduce an electrical device’s temperature by dispersing heat into the air, or a heat sink and fan combination may make up the CPU cooler. These cooling systems, which are typically referred to as air cooling, are frequently utilized in conjunction with airflow improvement systems.



