Screen flickering can be a headache, especially for gamers and individuals who spend long hours working on computers.
Understanding the causes behind screen flickering and knowing how to troubleshoot and resolve the problem can save you a lot of frustration.
Tips to Fix Screen Flickering Issues
In this blog post, we’ll explore seven tips to help you diagnose and fix screen flickering issues effectively.
1. Adjust the Refresh Rate
Cause: A mismatch between the refresh rate of your monitor and the settings on your computer.
Solution: Adjust the refresh rate to your monitor’s specifications.
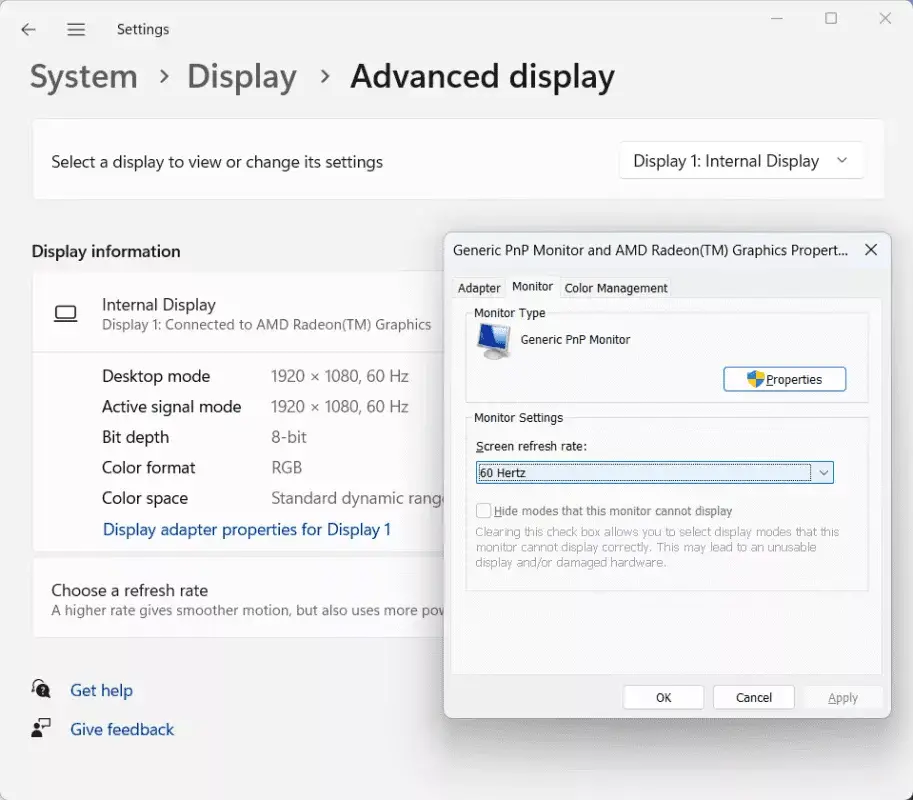
- Windows users should right-click on the desktop, choose “Display settings,” click “Advanced display settings,” select “Display adapter properties,” click the “Monitor” tab, and then adjust the refresh rate to the proper value.
- On macOS, open “System Preferences,” choose “Displays,” click the “Display” tab, and, if available, change the refresh rate.
2. Check for Software Compatibility Issues
Cause: Certain software applications conflicting with display settings.
Solution: Close or uninstall recently installed software that may be causing the flickering. Update the software to the latest version or check for any available patches that address compatibility issues.
In reality, it is more challenging to identify and address this issue. Simply keep this possibility in mind, then check out various communities, forums, or the software’s subreddit to see whether other users are having the same issue.
3. Update Graphics Drivers
Cause: Flickering on the screen may be caused by outdated or incompatible graphics drivers.
Solution: Install the most recent version of your graphics drivers.
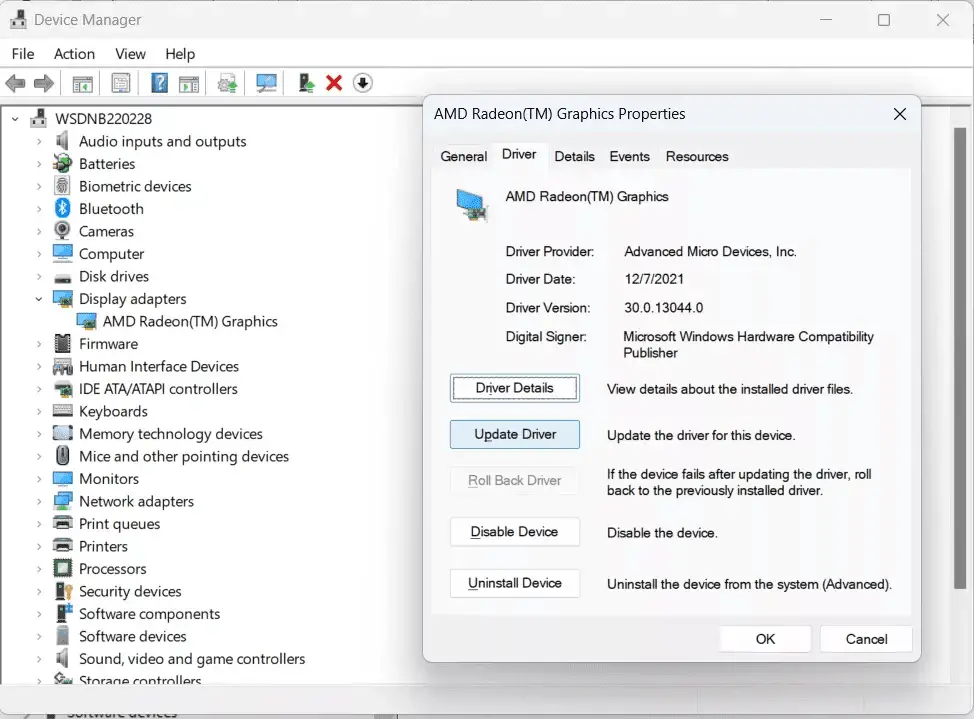
- When using Windows, right-click the desktop, choose “Display settings,” then “Advanced display settings,” “Display adapter properties,” “Driver” tab, and “Update Driver.”
- If a graphics driver update is available on macOS, go to “System Preferences,” choose “Software Update,” and then follow the on-screen instructions to install it.
4. Address Hardware Malfunction
Cause: Defective monitor, faulty graphics card, or unqualified intermediary devices (e.g., KVM switches).
Solution: Check the specifications and compatibility of your hardware components. Ensure they are functioning correctly and capable of supporting the required resolutions and refresh rates.
The entire setup is necessary for successful video signal transmission, and hardware is the most essential part. Hardware contains your computer, monitor, and any intermediary devices like an extender, KVM switch, docking hub, or adapter.
5. Check Cables and Connections
Cause: Loose, damaged, or unqualified cables or connectors between your computer and the monitor.
Solution:
- Ensure all cables are securely connected and properly seated.
- Try using different cables or connectors to rule out any cable-related issues.
- Verify if your cable supports the resolutions and refresh rates required for your setup, considering length limitations as well.
If you’re using a display with high resolutions/refresh rates, the connection between your PC and the monitor is most likely consuming its full bandwidth.
Signals may drop and become unstable if the length is too long. Check the cable’s specifications (perhaps an HDMI, DP, or VGA cable), including the resolutions, refresh rates, and transmission length limits.
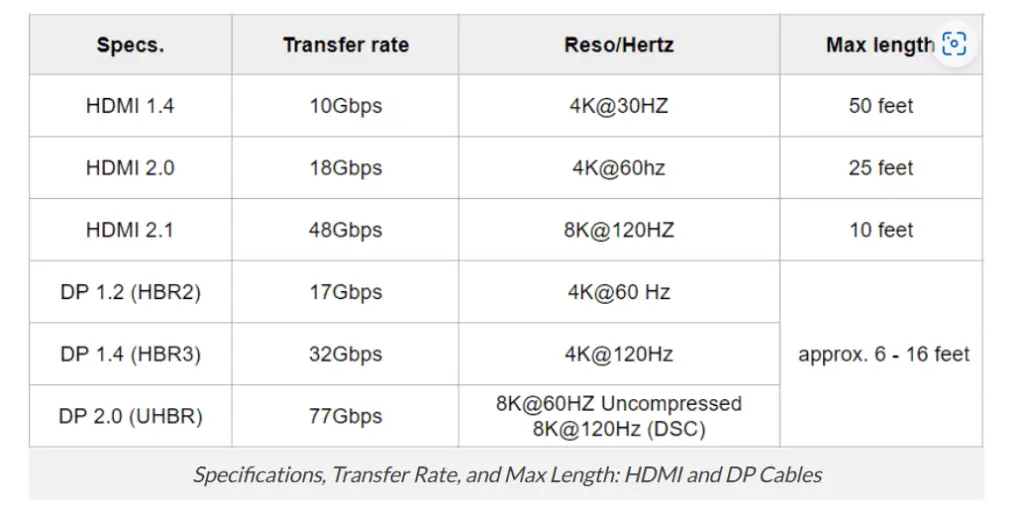
The specifications listed in the table are theoretical lab data for reference only; they might not be entirely accurate in actual use. Another point is that the maximum length may not always be included in the specifications itself, but instead heavily depends on the manufacturing quality and tolerances. In the actual world, you could require a better cable to properly manage the same problem.
6. Prevent Overheating
Cause: The monitor or graphics card may flicker as a result of excessive heat buildup. This can be caused by inadequate cooling, overlocking, or a high room temperature.
Solution:
- Ensure proper ventilation for your computer by cleaning dust or debris from cooling fans and vents.
- Consider using a cooling pad or external fan to maintain optimal temperatures.
- Avoid overclocking your components, as it can increase heat generation.
Yes, just like humans, machines could die from heat. Thermal throttling may be brought on by overheating. Modern computer parts include built-in safety features that shield them from excessive temperatures, like CPUs and graphics cards. They might alter their operation to produce less heat when they hit a specific temperature threshold, which would impair system performance and increase the likelihood of screen flickering.
Over time, the heat might actually harm things. The monitor, graphics card, CPU, or motherboard of your computer can all suffer damage from prolonged exposure to high temperatures. This harm may eventually show up as a flickering screen or other hardware failures.
7. Resolve Electrical Interference:
Cause: External devices or electromagnetic interference can cause screen flickering. Electrical interference can be a challenging problem to solve.
Solution:
- Identify and remove electronic devices or magnets near the affected area, if possible.
- If you suspect Wi-Fi router interference, reposition the router farther away from the computer, change the Wi-Fi channel, use a wired connection, and employ shielded cables or ferrite beads to minimize interference.
Conclusion
Screen flickering issues can be frustrating, but by following these seven tips, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve them.
Adjust the refresh rate, check cables and connections, update graphics drivers, address software compatibility issues, prevent overheating, and resolve electrical interference.
By applying these techniques, you can enjoy a flicker-free computing experience and get back to your work or gaming with ease.



