You may be familiar with the word DisplayPort if you’re new to the world of display interfaces.
When it comes to high-performance display interfaces, DisplayPort has emerged as a popular choice for gamers and graphic designers. Its versatility, high bandwidth, and robust capabilities make it an excellent option for those seeking top-notch visual experiences.
In this blog post, we will explore what is DisplayPort, and will explore its functionality, applications, different versions, connectors, and cables. Also, we will discuss about the key facts you should know about the DisplayPort interface and its relevance to gaming and graphic design.
DisplayPort
DisplayPort is a digital display interface developed by the VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association). It is designed to transmit high-definition audio and video signals from a computer or other source devices to displays, such as monitors or projectors.
DisplayPort has gained prominence as a successor to older analog video interfaces like VGA and DVI, offering enhanced performance and flexibility.
DisplayPort employs packet-based data transfer, which means it sends data in small packets, similar to how data is transmitted over the Internet.
How Does DisplayPort Work?
DisplayPort transmits audio and video signals using a unique signalling technology called “Micro-Packet Architecture.” It makes use of a main link, which transmits the majority of the data, and an auxiliary channel, which transmits other data including audio, control signals, and device identification.
In addition, DisplayPort enables features like High Bit Rate 3 (HBR3) for additional bandwidth, allowing for better resolutions and refresh rates, as well as Multi-Stream Transport (MST) for daisy-chaining multiple displays.
What is DisplayPort Used for?
DisplayPort is widely used in various industries, including gaming and graphic design, due to its exceptional capabilities. It provides high-resolution support, allowing for ultra-high-definition displays with resolutions up to 8K.
Additionally, DisplayPort supports high refresh rates, enabling smoother motion and reduced input lag for gamers. Its ability to transmit HDR content ensures accurate color reproduction and enhanced contrast, which is highly beneficial for graphic designers working with color-critical projects.
It is frequently used to connect to external monitors or projectors in computer systems, including laptops, desktops, and workstations.
Gamers and graphic designers who need high-resolution monitors and smooth graphics performance are particularly fond of DisplayPort. It is also used in professional settings like video editing studios, where accuracy and clear images are very important.
Different Versions of DisplayPort
DisplayPort has undergone several iterations, each introducing new features and improvements.
In order to make the most of these advanced features, it’s crucial to make sure your devices support compatible versions.
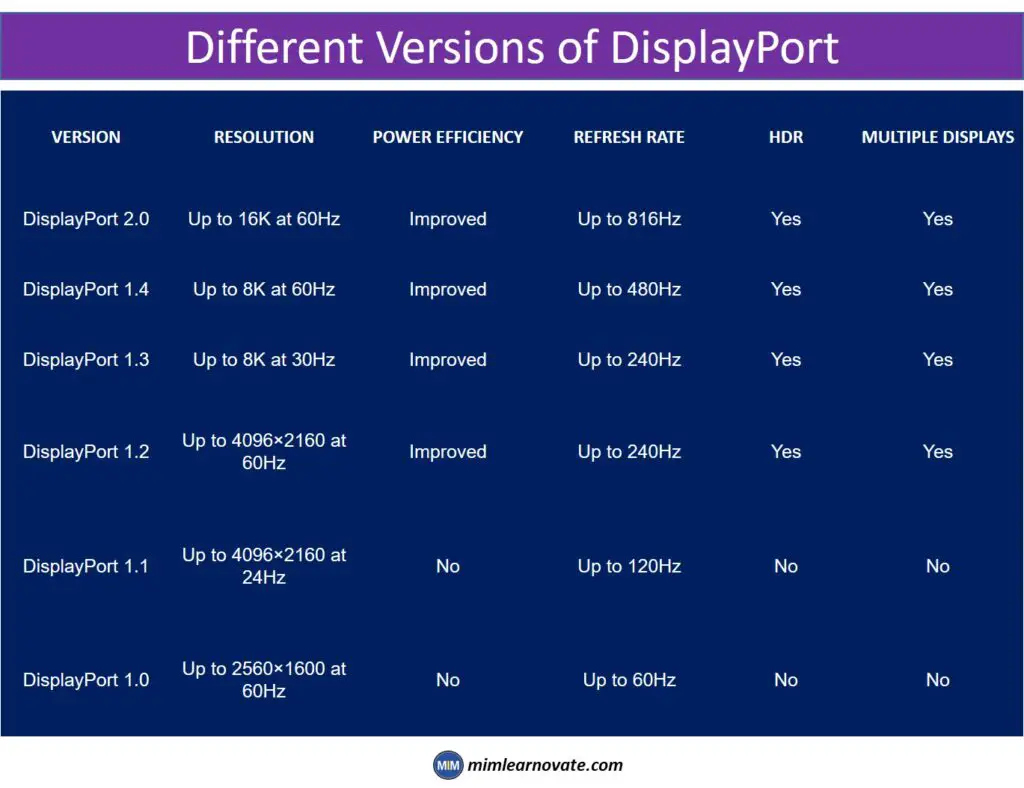
DisplayPort 1.0
This was the original DisplayPort version, which was released in 2006. Up to 2560 x 1600 resolutions at 60 Hz are supported.
DisplayPort 1.1
This version, which was released in 2007, included support for Dual-Mode DisplayPort, enabling it to be used with both DVI and HDMI displays. Additionally, HDCP 1.3 support was added.
DisplayPort 1.2
This version, released in 2010, provided support for higher resolutions and refresh rates. It can support resolutions of up to 2560 x 1600 at 120 Hz and 4096 x 2160 at 60 Hz.
Additionally, Display Stream Compression (DSC) support was added, allowing for the transmission of greater resolutions and refresh rates over a single DisplayPort cable.
DisplayPort 1.3
This version, which was released in 2014, boosted the maximum bandwidth to 32.4 Gbps and added support for HDR (High Dynamic Range). It also adds support for Multi-Stream Transport (MST), which allows many screens to be linked to a single DisplayPort output.
DisplayPort 1.4
This version, which was released in March 2016, includes support for higher resolutions and refresh rates, as well as brand-new features like HDR and Display Stream Compression (DSC).
DisplayPort 2.0
This version, which was released in 2019, now supports even higher resolutions and refresh rates. Resolutions of up to 8K at 60Hz and 16K at 30Hz are supported. New features like Dynamic HDR, Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), and Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) were also included with support.
DisplayPort 2.1
This version was released in 2022 and included support for even higher resolutions and refresh rates in addition to brand-new features like Dynamic HDR, Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), and Variable Refresh Rate (VRR).
| VERSION | RESOLUTION | POWER EFFICIENCY | REFRESH RATE | HDR | MULTIPLE DISPLAYS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DisplayPort 2.0 | Up to 16K at 60Hz | Improved | Up to 816Hz | Yes | Yes |
| DisplayPort 1.4 | Up to 8K at 60Hz | Improved | Up to 480Hz | Yes | Yes |
| DisplayPort 1.3 | Up to 8K at 30Hz | Improved | Up to 240Hz | Yes | Yes |
| DisplayPort 1.2 | Up to 4096×2160 at 60Hz | Improved | Up to 240Hz | Yes | Yes |
| DisplayPort 1.1 | Up to 4096×2160 at 24Hz | No | Up to 120Hz | No | No |
| DisplayPort 1.0 | Up to 2560×1600 at 60Hz | No | Up to 60Hz | No | No |
DisplayPort: Connectors and Cables
DisplayPort connectors come in various sizes, including:
- Standard DisplayPort
- Mini DisplayPort
- USB Type-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode
These connectors are designed to ensure a secure connection and provide compatibility across different devices.
DisplayPort cables are available in different lengths and types, such as standard DisplayPort cables, Mini DisplayPort cables, and DisplayPort to HDMI or DVI adapters, allowing for flexibility and compatibility with various display options.
DisplayPort or HDMI: Which is better?
The comparison between DisplayPort and HDMI depends on specific requirements and use cases.
Both interfaces have their strengths and are suitable for different scenarios. However, DisplayPort generally offers higher bandwidth, better support for high refresh rates, and more advanced features like Adaptive Sync technology.
These qualities make DisplayPort a preferred choice for gamers and graphic designers seeking the utmost visual quality and smoothness.
Read More: DisplayPort 1.4 vs. HDMI 2.1: Which Is Better for Gaming?
Contrarily, HDMI is more frequently used in home theatre systems and consumer electronics. In the end, the decision between DisplayPort and HDMI comes down to things like the devices you already possess and the functions you need.
Home theatre settings: HDMI is frequently the favored option for home theatre installations. HDMI is more compatible with consumer electronics because DisplayPort inputs aren’t available on many TVs.
Adapter Usage: Adapters can be used to connect a device with only an HDMI output to one with a DisplayPort input, or vice versa.
Laptop to TV/Projector Connections: Since HDMI is generally supported by most devices, it is a safe bet when connecting a laptop to a TV or projector.
Multiple Monitor Setups: DisplayPort is the preferred interface for connecting your laptop to multiple monitors. While DisplayPort enables daisy-chaining or the use of multi-stream transport (MST) to connect several monitors, HDMI typically supports a single screen.
Gaming Consoles and PC Gaming: The only output accessible on gaming consoles is often HDMI 2.0 or above, making it the preferred option. However, if your computer supports it, DisplayPort generally offers greater refresh rates and compatibility with cutting-edge gaming features, making it the preferable choice for PC gaming.
Read More: The 5 Best KVM Switches for Dual Monitors in 2023
To make a smart decision based on your unique demands and device compatibility, take into account these factors. Whether you use HDMI or DisplayPort, each has its own special benefits. Choosing the appropriate cable will guarantee top performance and improve your entire display experience.
Conclusion:
The DisplayPort interface is a powerful tool for gaming and graphic design enthusiasts, offering high-resolution support, HDR capabilities, and advanced features like Adaptive Sync technology. Its ability to handle demanding visual requirements makes it a reliable choice for those seeking exceptional image quality and smooth gameplay.
By understanding the fundamentals of DisplayPort, its working mechanism, and its various versions and connectors, gamers and graphic designers can make informed decisions when selecting display interfaces for their setups.



