A SWOT analysis is a popular business tool used to assess a company’s current state and determine its future direction. It examines the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing the business.
SWOT analysis is a tool that can assist you in identifying the current strengths of your business and developing a successful future strategy. SWOT analysis can also reveal areas of your business that are slowing you down or that your competitors may exploit if you don’t protect yourself.
In this blog post, we will explore the concepts of internal and external SWOT analysis and their significance in strategic decision-making.
SWOT analysis
The SWOT analysis method has been widely adopted in the business world since its inception at the Stanford Research Institute. SWOT analyses aim to understand the company’s position before making important decisions.
SWOT analysis is a method for evaluating a company’s performance, competition, risk, and potential as well as that of any division, product line, industry, or other entity that the company may have.
The technique can direct companies towards strategies more likely to be successful and away from those in which they have been, or are expected to be, less successful.
It uses both internal and external data. Independent SWOT analysts, investors, or competitors can also advise them on whether a firm, product line, or industry is strong or weak and why.
By analyzing the internal and external factors that influence a plan, product, campaign, or the business as a whole, the decision-making process becomes more straightforward.
A SWOT analysis should ideally provide a quick and simple exercise that offers valuable perspective. While it does not need to be overly detailed or time-consuming, you can certainly dive deep into your SWOT analysis if desired.
The acronym SWOT stands for:
Strengths: Internal factors that give an organization a competitive advantage.
Weaknesses: Internal factors that hinder an organization’s performance or put it at a disadvantage.
Opportunities: External factors that present potential avenues for growth and success.
Threats: External factors that pose challenges or risks to an organization’s operations.
By conducting a SWOT analysis, organizations can gain insights into their current state, make informed decisions, and develop strategies that align with their goals and objectives.
Internal SWOT Analysis
Internal SWOT analysis focuses on assessing an organization’s internal factors, which are within its control. It involves identifying the strengths and weaknesses that exist within the organization’s structure, resources, processes, and capabilities.
Internal analysis focuses on assessing strengths and weaknesses within the company.
It considers factors such as
- human resources (employees, customers, volunteers)
- physical resources (property, assets)
- financial resources (savings, debts, investments)
- processes (workflow methods, software, leadership)
Assessing Strengths
Identifying and leveraging an organization’s strengths is a crucial aspect of internal SWOT analysis. Strengths can include unique capabilities, valuable resources, a strong brand reputation, skilled workforce, efficient processes, or superior products or services.
By recognizing these internal strengths, organizations can capitalize on their competitive advantages and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Identifying Weaknesses
Internal SWOT analysis also involves identifying and addressing weaknesses within the organization. Weaknesses may include outdated technology, limited resources, inadequate skills or expertise, inefficient processes, or a lack of competitive differentiation.
By acknowledging and addressing these weaknesses, organizations can implement improvement strategies and enhance their overall performance.
External SWOT Analysis
External SWOT analysis focuses on evaluating the external factors that impact an organization’s operations and market positioning. It involves examining the opportunities and threats present in the external environment.
External analysis, on the other hand, explores opportunities and threats outside the company.
It takes into account
- regulatory factors (environmental, economic, political)
- demographics (customer characteristics, urbanization)
- economic trends (global economy, market volatility)
- market shifts (technological advancements, new competitors)
- critical relationships (suppliers, partners)
Exploring Opportunities
Opportunities arise from external factors that organizations can leverage to achieve growth and success.
These factors can include emerging markets, technological advancements, changing customer preferences, industry trends, or new partnerships.
By identifying and capitalizing on these opportunities, organizations can expand their market reach, introduce new products or services, or enter new markets.
Analyzing Threats
Threats refer to external factors that can hinder an organization’s performance or pose risks to its operations. These factors can include intense competition, economic downturns, regulatory changes, disruptive technologies, or shifting consumer demands.
By analyzing and understanding these threats, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate risks, adapt to changing circumstances, and maintain their competitiveness.
Example: Internal and External SWOT Analysis
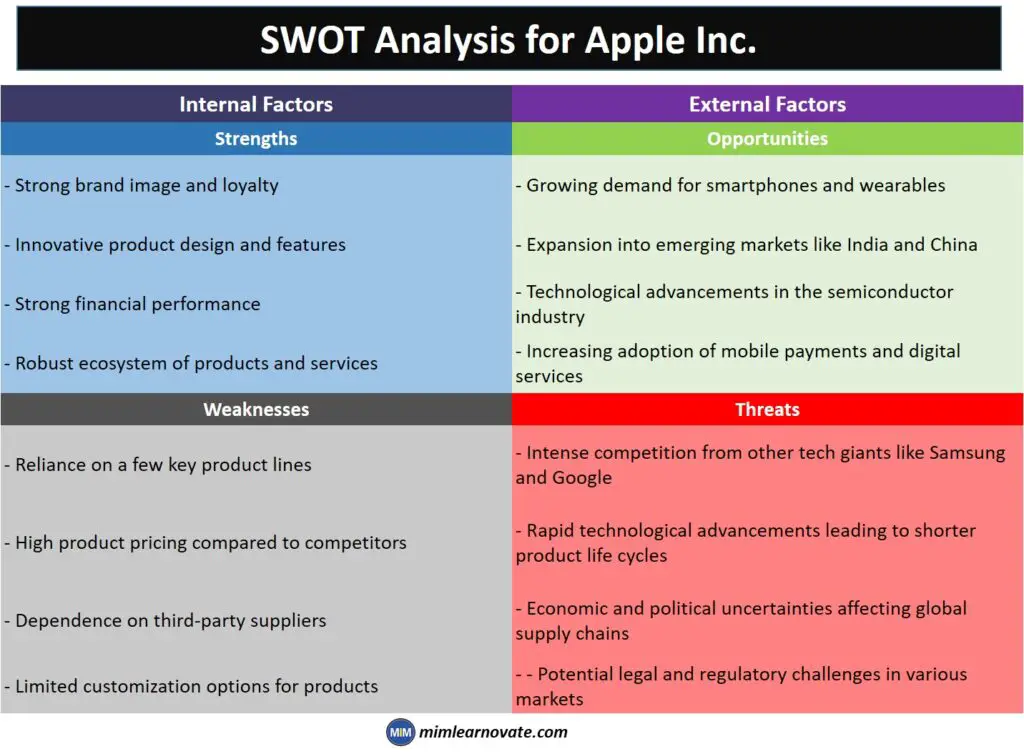
SWOT Analysis: Example for Apple Inc.
| Internal Factors | External Factors |
|---|---|
| Strengths | Opportunities |
| – Strong brand image and loyalty | – Growing demand for smartphones and wearables |
| – Innovative product design and features | – Expansion into emerging markets like India and China |
| – Strong financial performance | – Technological advancements in the semiconductor industry |
| – Robust ecosystem of products and services | – Increasing adoption of mobile payments and digital services |
| Weaknesses | Threats |
| – Reliance on a few key product lines | – Intense competition from other tech giants like Samsung and Google |
| – High product pricing compared to competitors | – Rapid technological advancements leading to shorter product life cycles |
| – Dependence on third-party suppliers | – Economic and political uncertainties affecting global supply chains |
| – Limited customization options for products | – Potential legal and regulatory challenges in various markets |
In example, SWOT analysis is conducted for Apple Inc., a leading technology company.
The internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) reflect Apple’s core competencies, including its strong brand image, innovative product design, financial performance, and ecosystem of products and services.
These internal strengths provide Apple with a competitive advantage.
The external factors (opportunities and threats) represent the market conditions and external influences that can impact the company’s performance.
Apple has opportunities to capitalize on the growing demand for smartphones and wearables, expand into emerging markets, leverage technological advancements, and benefit from the increasing adoption of mobile payments. However, Apple also faces threats from intense competition, rapid technological advancements, global economic and political uncertainties, and potential legal and regulatory challenges.
This SWOT analysis helps Apple understand its internal capabilities and external market dynamics, guiding its strategic decision-making process.
Importance of Internal and External SWOT Analysis
Internal and external SWOT analyses play vital roles in strategic decision-making for organizations.
By conducting an internal analysis, organizations can identify their strengths to build upon and weaknesses to address, allowing them to optimize their internal resources and capabilities. The external analysis helps organizations identify opportunities to capitalize on and threats to mitigate, enabling them to navigate the external environment effectively.
The internal and external analysis is intertwined within the SWOT analysis itself. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors, including elements such as the team, assets, and resources. Strengths may include a productive workforce, valuable expertise, or a strong customer base, while weaknesses can arise from an aging workforce or an inability to meet consumer demand.
On the other hand, opportunities and threats are external factors that affect the analysis. These factors are beyond the company’s control and can significantly impact its operations. Opportunities may arise from market trends, emerging technologies, or favorable regulatory changes. Threats can come from intense competition, economic fluctuations, or changing consumer preferences.
Conclusion
By analyzing internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats, businesses can make informed decisions and chart a successful course for the future.
SWOT analysis serves as a valuable tool for organizations seeking to gain a deeper understanding of their internal strengths and weaknesses while navigating the ever-changing external business landscape.
The continuous evaluation and adaptation of these analyses enable organizations to stay agile and thrive in a dynamic and competitive environment.
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about marketing.
Management
- Human Resource Management
- Management Information System
- Why is Information Governance Important?
- How Data Analysis Is Changing Information Governance?
- The St. Gallen Management Model
- System-Oriented Management
- Tools Transforming Knowledge Management
- Levels of Management
- Information Management Software
- Tools for Information Management
- Information Governance vs Records Management
- Management Information System Books
- Greenwashing: A Case Study on DWS
- Greenwashing Examples
Statistics
Marketing
- Strategic marketing planning
- Marketing Environment
- Consumer buying decision process
- Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
- Product Positioning
- Target Market Strategies
- Market Segmentation
- STP Process
- Data Analysis Process
- Consumer Adoption Process
- Branding
- Product Life Cycle
- Product Attributes
- Price Discrimination
- Service-Based
- Company Vs. Product-Based Company
- Product Classification
- Penetration Pricing and Price Skimming
- Case Study of Nestle
- Fast-Moving Consumer Goods
- Motorola’s Customer-Defined, ‘Six-Sigma Quality
- PEST And a SWOT Analysis
- Web Design Company Vs. a Web Designer
- Internal and External SWOT Analysis
- Strategic Opportunism
Marketing Analysis
ChatGPT
- ChatGPT For Keyword Research
- Prompts for New Business Idea Generation
- ChatGPT Business Entrepreneur
- Learn Languages with ChatGPT
- Use ChatGPT on WhatsApp
- ChatGPT as Virtual Research Assistant
- ChatGPT for Meta-Analysis in Research
- ChatGPT For Large Documents
- ChatGPT for Hypothesis Development
- ChatGPT for Text Analysis
- ChatGPT to Write Code in Python
- ChatGPT to Write Literature Review
- Books ChatGPT



