In this article we will look at 5 stages of consumer buying decision process. Clearly the buying process starts long before actual purchase and continues long after. This encourages marketers to concentrate on the full buying process rather than just the purchase decision.
Most huge companies conduct extensive research on consumer purchasing decisions in order to answer questions about what customers buy, where they buy, how and how much they buy, when they buy, and why they buy.
Marketers can investigate consumer purchases to answer questions about what people buy, where they buy it, and how much they pay. However, understanding the whys of consumer purchasing behavior and the purchasing decision process is difficult because the answers are frequently sealed within the consumer’s head.
Consumer buying decision process
A buying decision process is the process customers goes through when buying a product. It is a series of steps that a consumer takes to make a purchasing decision.
To demonstrate this concept, we will use a consumer as an example and try to understand how he became interested in purchasing a camera and the stages he went through to reach the final decision.
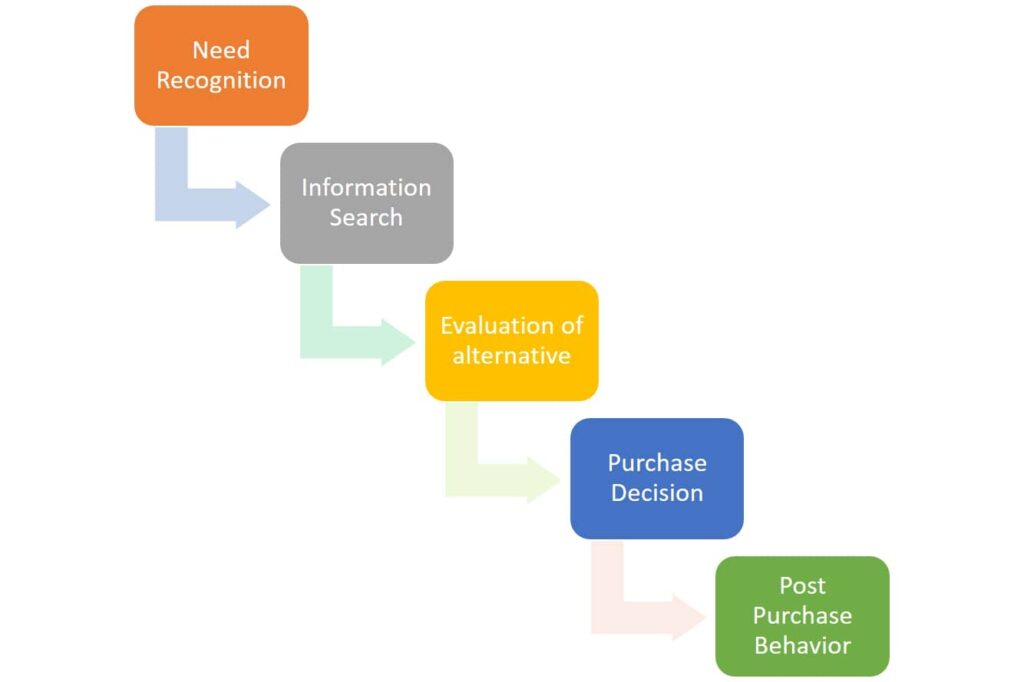
Stages of consumer buying decision process
Following steps are involved in consumer buying decision process.
1- Need Recognition
2- Information Search
3- Evaluation of alternative
4- Purchase decision
5- Post purchase behavior
1- Need Recognition
The buying process begins with need recognition, which occurs when the buyer recognizes a problem or need.
The customer detects a distinction between his or her current state and a desired state. A purchase cannot take place without recognition of the need. Consumer’s need may have been triggered by internal stimuli such as hunger or external stimuli such as advertising.
Internal stimuli
Internal stimuli can trigger the urge when one of the person’s basic needs ( hunger, thirst, sex ) escalates to a degree high enough to become a drive. The person has learnt how to deal with this urge from previous experience and is attracted toward objects that he or she knows would fulfil it.
External stimuli
External stimuli can also trigger a need. The consumer walks through a bakery and the scent of freshly made bread makes him hungry; he admires a neighbor’s new car; or he watches a television commercial for a Asian trip. At this point, the marketer must identify the circumstances and events that typically cause customer need recognition.
The marketer should conduct consumer research to determine what kind of needs or problems occur, what causes them, and how they led the consumer to this specific product.
Example of Need Recognition
User wants to connect with family and friends. The need of being connected is fulfilled by purchasing a smartphone.
Consumer may respond that she thought she required a camera after seeing images taken on vacation by friends. By obtaining such information, the marketer can discover the triggers that most frequently trigger interest in the product and build marketing programs that incorporate these stimuli.
2- Information Search
Search all the possible data about the product that the consumer is purchasing. Customer may visit retail outlet to check product or search product online. Product recommendations can be taken from the people who own the product.
- The consumer search for online reviews
- The consumer see pros and cons of the product or service which he is buying and then he will make decision to buy.
Consumer may obtain Information through many sources including:
- Magazines, internet, mass media, consumer-rating organizations. ( public sources )
- Family, friends, neighbors, acquaintances ( personal sources )
- Ads , salespeople, advertising, dealers, packaging, displays. ( commercial sources )
- Handling, examining, using the product ( experiential sources )
Internal Search
Internal search refers to recalling past experiences with product.
The consumer’s awareness and knowledge of available brands and features grows as more information is received.
Example of Information Search
Here, the consumer becomes more attentive to camera information. He is drawn to camera advertisements, cameras used by colleagues, friends and camera discussions. Alternatively, he may engage in active information search, in which he searches for reading material, calls acquaintances, and acquires information in other ways.
The quantity of searching he performs will be determined by his motivation, the amount of information he starts with, the ease with which he may access more information, the value he places on extra information, and the satisfaction he gets from searching.
3- Evaluation of alternative
How do consumers choose brands? The marketer must understand alternative evaluation, or how consumers choose brands.
Each consumer wants to satisfy a demand and gain specific benefits from a product or service. Each consumer sees a product as a bundle of attributes with variable capacity to give advantages and meet needs. It is buyer decision stage in which the consumer evaluates alternative brands.
Secondly, consumers value each quality differently. When asked about a product’s features, consumers think about salient attributes. But these aren’t always consumers’ top priorities.
Also, consumers may create brand beliefs regarding each brand’s attributes. Brand image refers to a brand’s beliefs. Consumer views may differ from genuine attributes depending on experience and selective perception, distortion, and retention.
Consumers evaluate different products / brands on the basis of varying product attributes and whether that can deliver the benefits that customers are seeking.
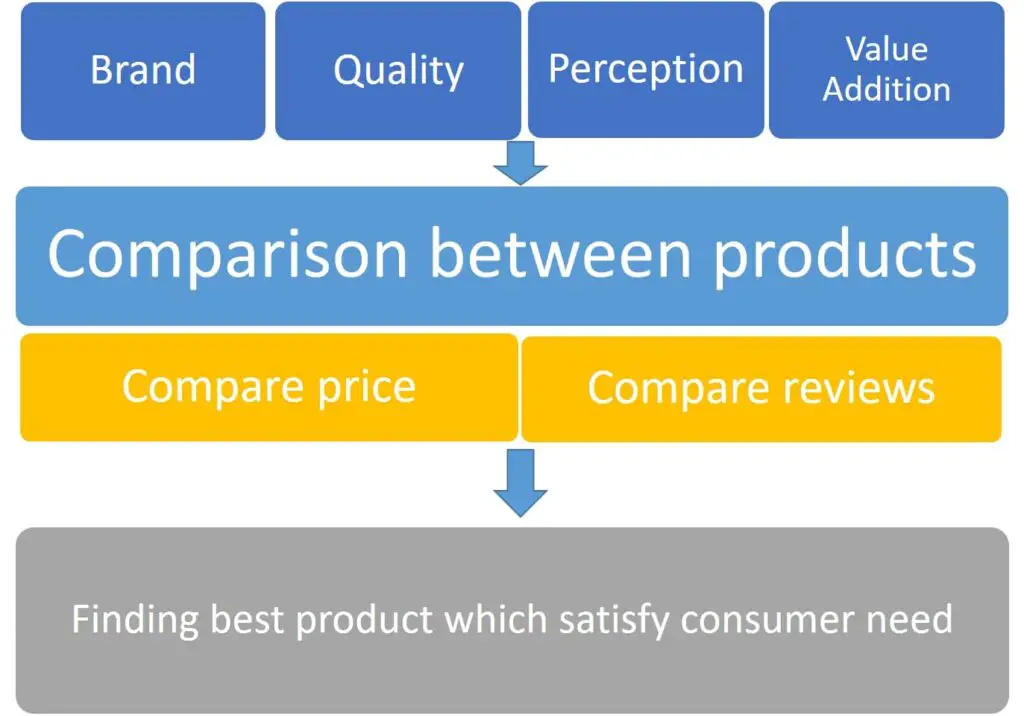
- Consumer evaluate different options available in market based on brand, quality, perception and value addition.
- Comparison between products / Compare price / Compare reviews
- Consumer spends most of his time in this stage as it is time consuming because he wants to find best product which satisfy his need.
Example of Evaluation of alternative
Picture quality, ease of use, camera size, price, and other aspects may be evaluated for cameras. The consumer may expect his camera satisfaction to grow with better picture duality, a medium-weight camera against a very light or extremely heavy one, and a small 35 mm camera over a single lens reflex camera with interchangeable lenses. Combining his best attributes creates his ideal camera. If affordable, the consumer would prefer the camera.
4- Purchase decision
The consumer really purchases the product at this point whether online or going to the store. A consumer will typically choose their most preferred brand, but there are two elements to consider:
- Purchase intentions
- Purchase decision
The consumer’s purchase intention may be influenced by elements like usual income, usual pricing, and typical product advantages.
5- Post purchase behavior
When a customer purchases a product, the marketer’s job is not finished. The consumer will express their satisfaction or dissatisfaction with the product after buying it by engaging in post purchase behaviour that the marketer finds interesting.
What factors into a customer’s satisfaction or dissatisfaction with a purchase?
The link between consumer expectations and the product’s perceived performance holds the key to the solution.
Consumers experience disappointment when a product doesn’t live up to their expectations, satisfaction when it does, and ecstasy when it exceeds those expectations.
The messages that buyers receive from merchants, friends, and other information sources serve as the foundation for their expectations.
Customer will compare products with their previous expectation and will either be satisfied or dissatisfied.
This can greatly effect the decision process for similar purchases from the same company.
If consumer is satisfied with product
✅ Suggest and recommend
✅ Positive WOM (Word of Mouth)
✅ Serve as a brand Ambassador
If consumer is dissatisfied with product
❌ Will not suggest to anyone
❌ Negative WOM (Word of Mouth)
❌ Spoil brand image
Example of Post purchase behavior
Consumer may like the camera that he has purchase and recommend to others or dissatisfy with his purchase.
Toyota congratulates new car owners on their choice of a superb car by writing or calling them. It airs commercials with happy customers praising their new cars. love what you do for me, Toyota ! Toyota collects consumer feedback for enhancements and provides a list of service facilities to monitor post-purchase behavior.
Conclusion
Successful marketing is built on an understanding of the needs and purchasing process of the consumer. By understanding how consumers go through need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, the purchase decision and post purchase behaviour, the marketer can pick up many clues as to how to meet the buyer’s needs.
The marketer can create an efficient program to promote an appealing offer to the target market by comprehending the numerous participants in the buying process and the biggest affects on their purchasing behavior.
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about marketing.
Management
- Human Resource Management
- Management Information System
- Why is Information Governance Important?
- How Data Analysis Is Changing Information Governance?
- The St. Gallen Management Model
- System-Oriented Management
- Tools Transforming Knowledge Management
- Levels of Management
- Information Management Software
- Tools for Information Management
- Information Governance vs Records Management
- Management Information System Books
- Greenwashing: A Case Study on DWS
- Greenwashing Examples
Statistics
Marketing
- Strategic marketing planning
- Marketing Environment
- Consumer buying decision process
- Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
- Product Positioning
- Target Market Strategies
- Market Segmentation
- STP Process
- Data Analysis Process
- Consumer Adoption Process
- Branding
- Product Life Cycle
- Product Attributes
- Price Discrimination
- Service-Based
- Company Vs. Product-Based Company
- Product Classification
- Penetration Pricing and Price Skimming
- Case Study of Nestle
- Fast-Moving Consumer Goods
- Motorola’s Customer-Defined, ‘Six-Sigma Quality
- PEST And a SWOT Analysis
- Web Design Company Vs. a Web Designer
- Internal and External SWOT Analysis
- Strategic Opportunism
Marketing Analysis
ChatGPT
- ChatGPT For Keyword Research
- Prompts for New Business Idea Generation
- ChatGPT Business Entrepreneur
- Learn Languages with ChatGPT
- Use ChatGPT on WhatsApp
- ChatGPT as Virtual Research Assistant
- ChatGPT for Meta-Analysis in Research
- ChatGPT For Large Documents
- ChatGPT for Hypothesis Development
- ChatGPT for Text Analysis
- ChatGPT to Write Code in Python
- ChatGPT to Write Literature Review
- Books ChatGPT




1 Comment
Reading your article helped me a lot and I agree with you. But I still have some doubts, can you clarify for me? I’ll keep an eye out for your answers.