In the world of research and experimentation, variables play a crucial role in studying and analyzing relationships between different factors.
In studies to test cause-and-effect relationships, researchers frequently manipulate or measure independent and dependent variables.
The relationship between these variables helps researchers uncover valuable insights and advance knowledge in their respective fields. By understanding the significance of independent and dependent variables, researchers can design robust experiments, draw meaningful conclusions, and contribute to the advancement of scientific understanding.
So, let’s explore what is independent and dependent variables and explore their differences.
10 Types of Variables in Research | Examples
independent variable
An independent variable is the variable that the researcher manipulates or controls. It is the factor that is intentionally changed to observe its effects on the dependent variable.
In other words, it is the cause or predictor variable.
In an experimental study, an independent variable is one that you change or alter to examine its effects. It is named “independent” because it is unaffected by any other study variables.
What is an Independent Variable?
Other names for independent variables include:
- Explanatory variables (those that explain the event or outcome)
- Predictor variables (they can be used to predict the value of a dependent variable)
- Right-hand-side variables are those that are found on the right side of a regression equation.
dependent variable
Dependent variable is the variable that is observed or measured. It is the outcome or response variable that researchers are interested in understanding or predicting. The dependent variable is influenced by the independent variable and is typically measured or observed during an experiment.
A dependent variable is one that is altered as a result of the change of an independent variable. Your independent variable “depends” on the outcome you’re interested in measuring.
Dependent Variable in Research: Examples
Dependent variables are also referred to as:
- Response variables (they respond when one variable changes)
- Outcome variables (they stand in for the result you want to measure)
- Left-hand-side variables are those that appear on the left side of a regression equation.
After changing the independent variable, you record the dependent variable. By performing statistical analyses, you can use this measurement data to determine whether and how much your independent variable affects the dependent variable.
You can calculate the extent to which changes in your independent variable influence changes in your dependent variable based on your findings. Additionally, you can forecast how much change in the independent variable will affect your dependent variable.
The relationship between the independent and dependent variables is at the core of research analysis. By manipulating the independent variable, researchers can observe its impact on the dependent variable.

Operationalization of Variables Examples | Benefits, Drawbacks
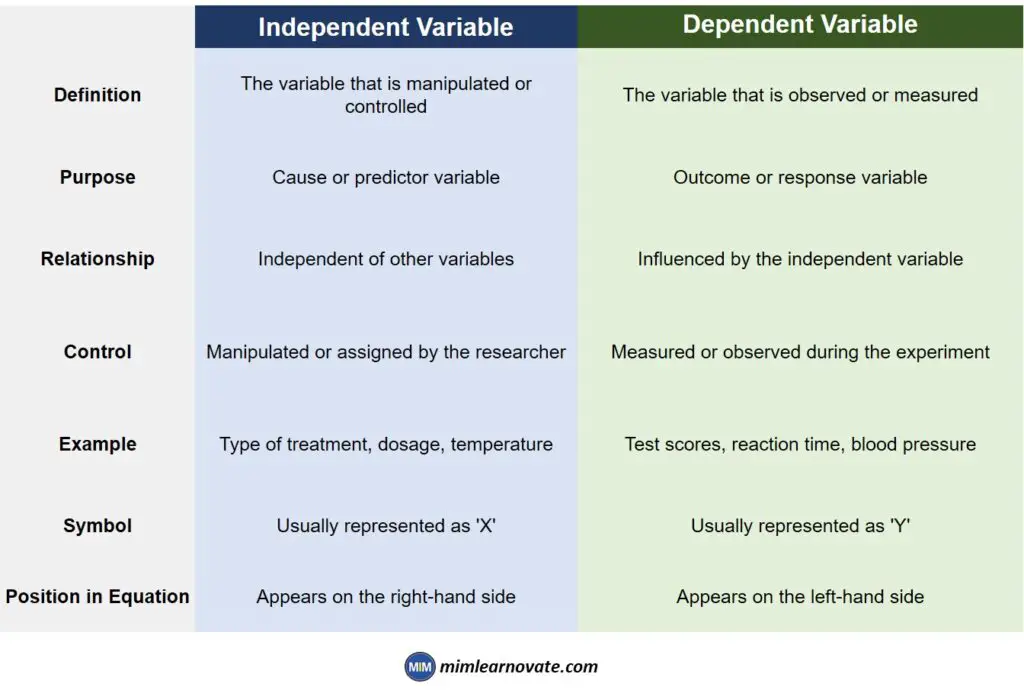
Independent vs. Dependent Variable
| Independent Variable | Dependent Variable | |
| Definition | The variable that is manipulated or controlled | The variable that is observed or measured |
| Purpose | Cause or predictor variable | Outcome or response variable |
| Relationship | Independent of other variables | Influenced by the independent variable |
| Control | Manipulated or assigned by the researcher | Measured or observed during the experiment |
| Example | Type of treatment, dosage, temperature | Test scores, reaction time, blood pressure |
| Symbol | Usually represented as ‘X’ | Usually represented as ‘Y’ |
| Position in Equation | Appears on the right-hand side | Appears on the left-hand side |
Difference between Independent and Dependent Variable
Independent Variable
- Manipulated or controlled by the researcher.
- Represents the potential cause or predictor of an outcome.
- Can be changed or varied to observe its effect on the dependent variable.
- Typically represented as ‘X’ in equations or research studies.
- Examples include treatment type, dosage, temperature, or instructional method.
Dependent Variable
- Observed or measured by the researcher.
- Represents the outcome or response that is influenced by the independent variable.
- The variable of interest that researchers aim to understand or predict.
- Usually represented as ‘Y’ in equations or research studies.
- Examples include test scores, reaction time, blood pressure, or survey responses.
Independent vs. Dependent Variable: Relationship
- Independent variables are independent of other variables and can be manipulated.
- Dependent variables are dependent on the independent variable and can change based on its manipulation.
- The relationship between these variables helps establish cause-and-effect associations.
Independent vs. Dependent Variable: Position
- Independent variables typically appear on the right-hand side of equations or research designs.
- Dependent variables typically appear on the left-hand side of equations or research designs.
How to Control Extraneous Variables?
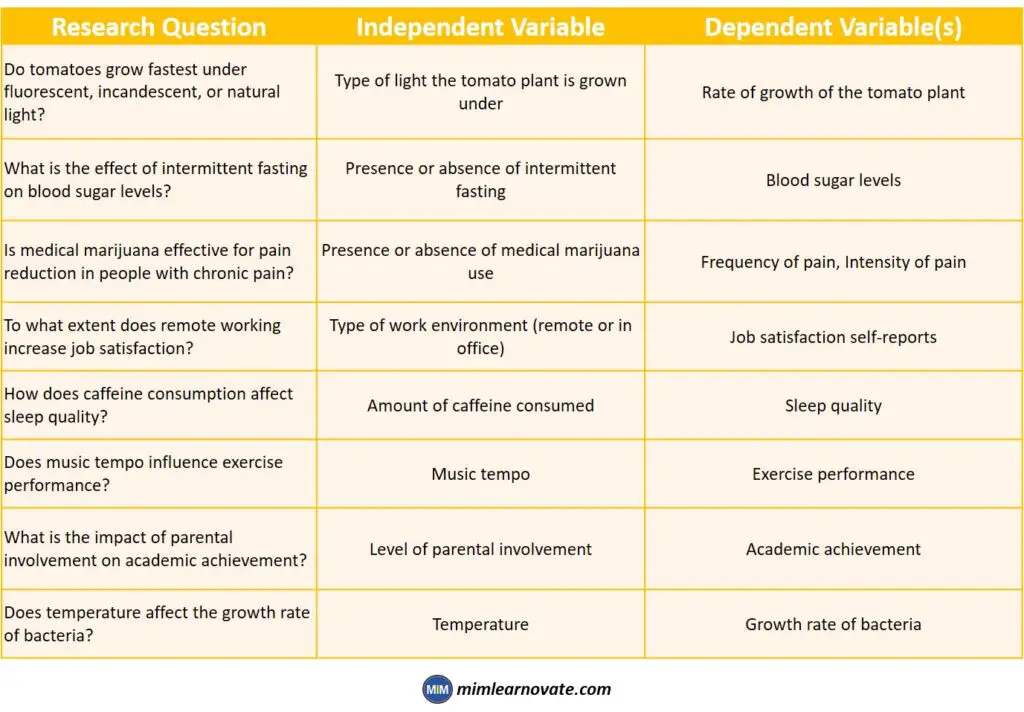
Independent vs. Dependent Variable: Example
| Research Question | Independent Variable | Dependent Variable(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Do tomatoes grow fastest under fluorescent, incandescent, or natural light? | Type of light the tomato plant is grown under | Rate of growth of the tomato plant |
| What is the effect of intermittent fasting on blood sugar levels? | Presence or absence of intermittent fasting | Blood sugar levels |
| Is medical marijuana effective for pain reduction in people with chronic pain? | Presence or absence of medical marijuana use | Frequency of pain, Intensity of pain |
| To what extent does remote working increase job satisfaction? | Type of work environment (remote or in office) | Job satisfaction self-reports |
| How does caffeine consumption affect sleep quality? | Amount of caffeine consumed | Sleep quality |
| Does music tempo influence exercise performance? | Music tempo | Exercise performance |
| What is the impact of parental involvement on academic achievement? | Level of parental involvement | Academic achievement |
| Does temperature affect the growth rate of bacteria? | Temperature | Growth rate of bacteria |
This table provides examples of various research questions and the corresponding independent and dependent variables involved. Researchers use these variables to investigate relationships, understand causal effects, and gain insights into specific phenomena within their fields of study.
Research Design | Importance, Types of Research Design Examples
Conclusion
In summary, independent variables are the factors that researchers manipulate, while dependent variables are the outcomes or responses they observe or measure.
Understanding the distinction between independent and dependent variables is crucial in research. Researchers manipulate the independent variable to observe its influence on the dependent variable, allowing them to study and explain relationships, make predictions, and draw meaningful conclusions.
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about research methodology.
Comparision
- Basic and Applied Research
- Cross-Sectional vs Longitudinal Studies
- Survey vs Questionnaire
- Open Ended vs Closed Ended Questions
- Experimental and Non-Experimental Research
- Inductive vs Deductive Approach
- Null and Alternative Hypothesis
- Reliability vs Validity
- Population vs Sample
- Conceptual Framework and Theoretical Framework
- Bibliography and Reference
- Stratified vs Cluster Sampling
- Sampling Error vs Sampling Bias
- Internal Validity vs External Validity
- Full-Scale, Laboratory-Scale and Pilot-Scale Studies
- Plagiarism and Paraphrasing
- Research Methodology Vs. Research Method
- Mediator and Moderator
Comparision
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable – MIM Learnovate
- Research Article and Research Paper
- Proposition and Hypothesis
- Principal Component Analysis and Partial Least Squares
- Academic Research vs Industry Research
- Clinical Research vs Lab Research
- Research Lab and Hospital Lab
- Thesis Statement and Research Question
- Quantitative Researchers vs. Quantitative Traders
- Premise, Hypothesis and Supposition
- Survey Vs Experiment
- Hypothesis and Theory
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable
- APA vs. MLA
- Ghost Authorship vs. Gift Authorship
Research
- Research Methods
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research
- Survey Research
- Conclusive Research
- Descriptive Research
- Cross-Sectional Research
- Theoretical Framework
- Conceptual Framework
- Triangulation
- Grounded Theory
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Mixed Method
- Correlational Research
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Stratified Sampling
- Ethnography
- Ghost Authorship
- Secondary Data Collection
- Primary Data Collection
- Ex-Post-Facto
Research
- Table of Contents
- Dissertation Topic
- Synopsis
- Thesis Statement
- Research Proposal
- Research Questions
- Research Problem
- Research Gap
- Types of Research Gaps
- Variables
- Operationalization of Variables
- Literature Review
- Research Hypothesis
- Questionnaire
- Abstract
- Validity
- Reliability
- Measurement of Scale
- Sampling Techniques
- Acknowledgements
Statistics