You can better comprehend the relationship between two variables in research with the help of mediators and moderators. The differences between a mediator and a moderator are discussed in this article.
You’ll find that mediating and moderating variables provide more than just a simple study when you learn about them. They give an insight look into real problems. This is due to the fact that the mediator and moderator variables perform the following functions:
- Identify the relationship between the variables.
- Assess the external validity of your research.
- Analyze correlations and causal relationships between two variables.
To begin, it is important to realize that both variables aim to illustrate the relationship between an independent and dependent variable. In this sense, both mediation and moderation involve examining how a third variable fits into that relationship.
Mediator
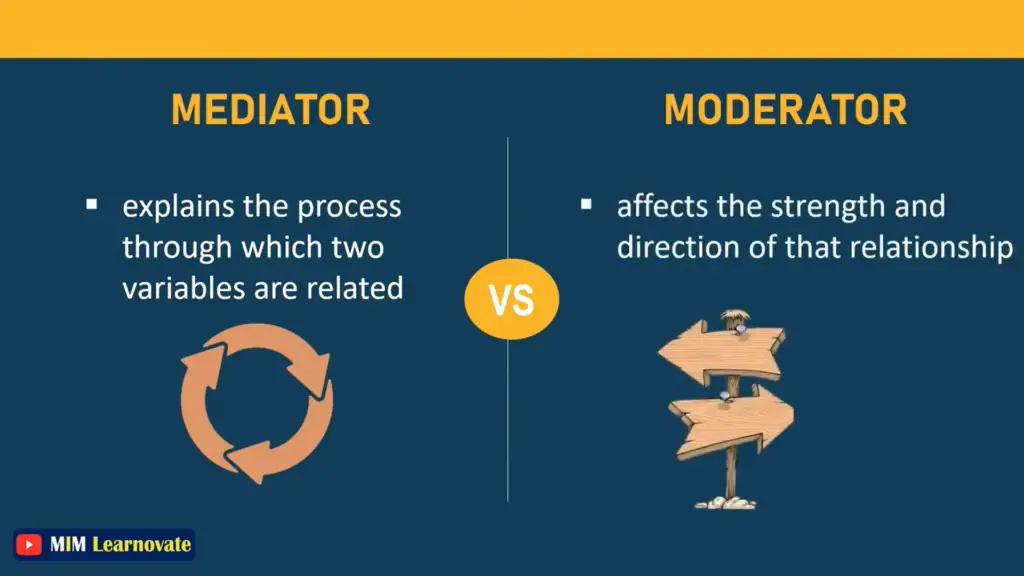
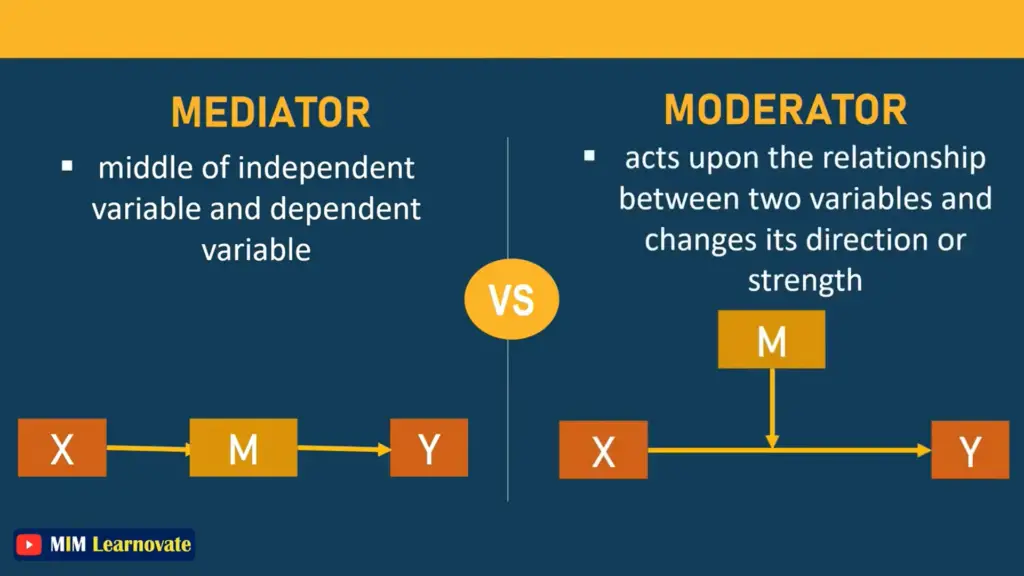
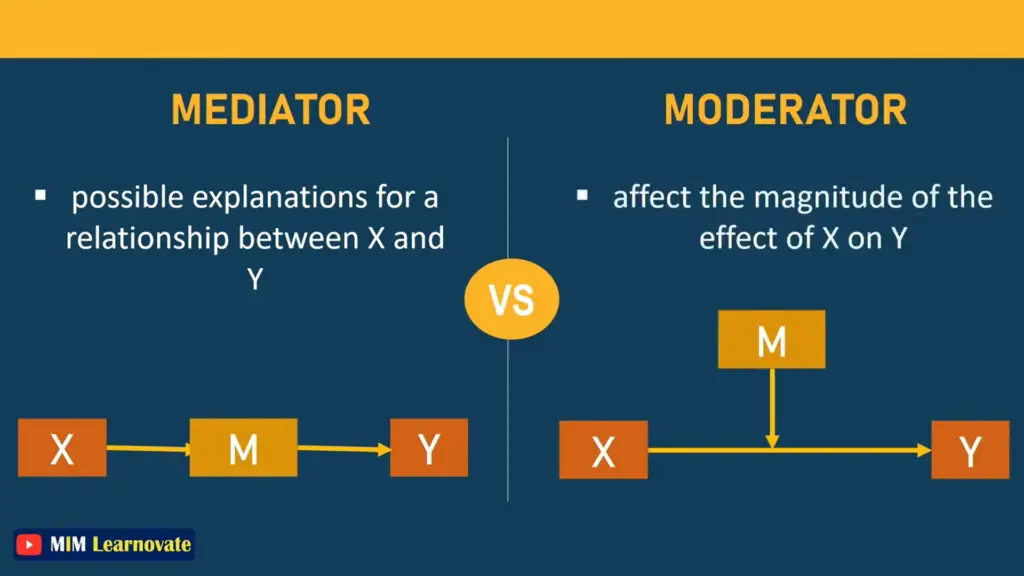
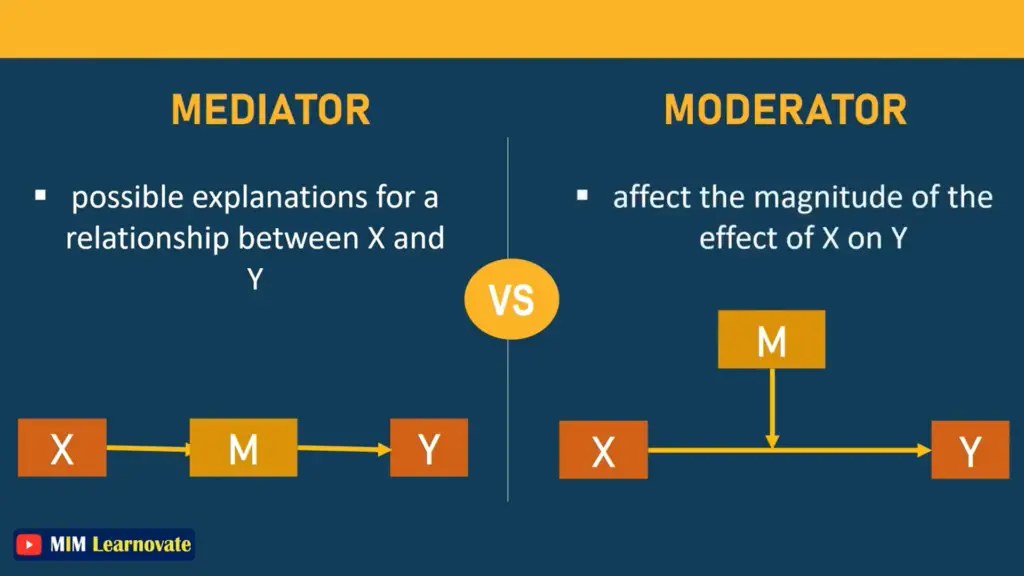
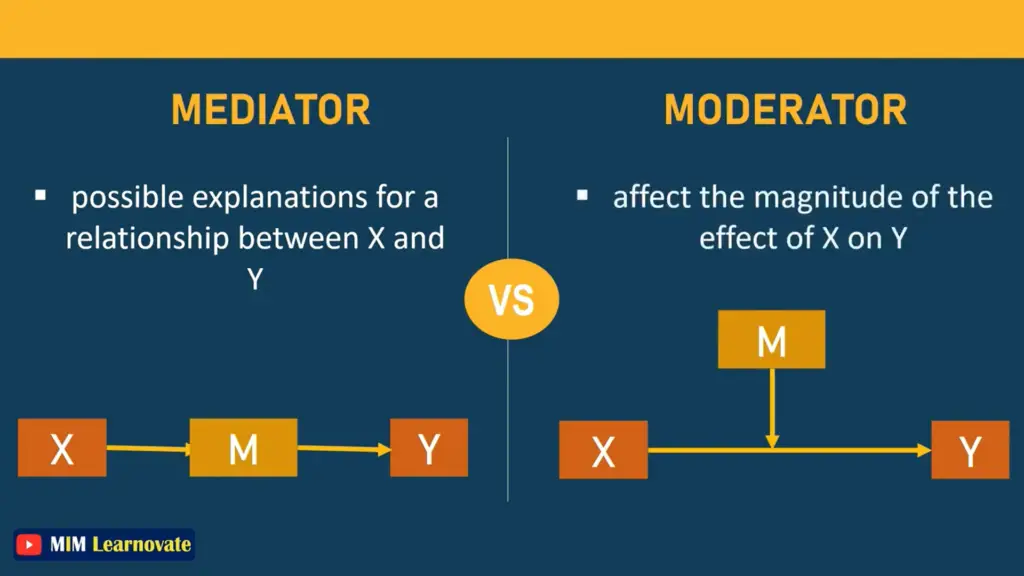
A mediator mediates the relationship between the independent and dependent variables, providing an explanation for why such a relationship exists. mediator variable carries an effect. In a complete mediation, an independent variable causes the mediator variable to change in some way, which then causes the dependent variable to change.
The relationship between the variables, including how they are related and the nature of their relationship, is shown by the mediating variable.
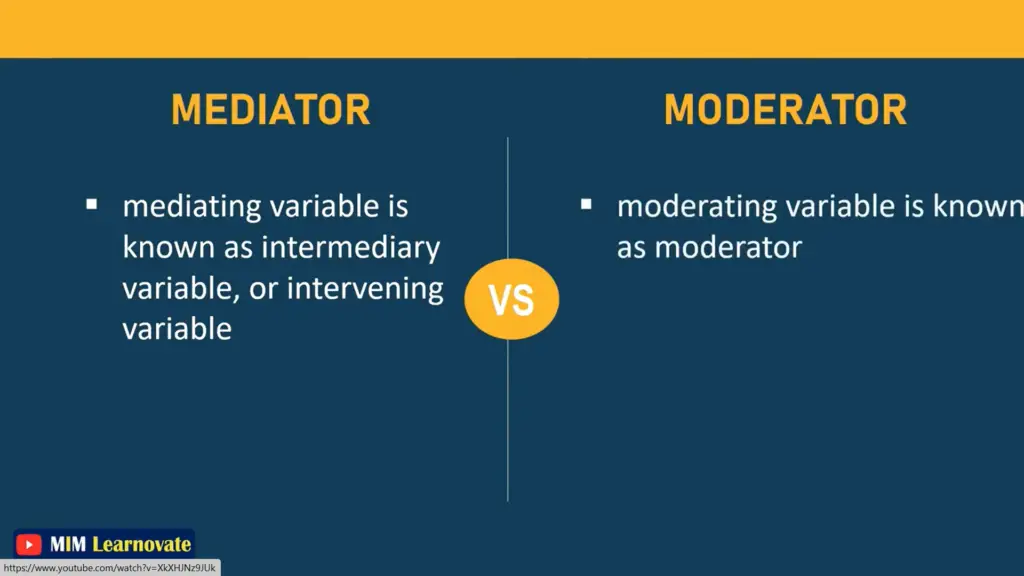
In order to explain properly, we might identify the mediating variable as an intervening variable, which comes between the two variables and shows that how these variables are related.
Example of Mediator
To determine whether the mediator has a significant impact than the independent variable itself, mediation analysis is used.
The temperature on a cooker is an evident real-life mediator. Water won’t begin to boil until the cooker is turned on, but the heat that results from turning the cooker knob is what actually causes the water to boil.
To test this, we could evaluate how closely the state of the water— whether it is boiling—relates to the knob being turned. We can consider such a weak correlation because there would be no effect for the first few minutes.
We can see that, in contrast to the relationship between the state of the water and the temperature of your stove, it is the stove’s temperature (the mediator) that is causing the water to boil, not simply the action of turning a knob (the independent variable). Comparing the strength of these effects provides you with insight into what’s truly carrying the effect on the water (the dependent variable).
Moderator
The moderator is the variable that influences or directs the overall relationship between two variables. The moderating variable affects the relationship between the variables and has the power to either increase or decrease the strength of the relationship between the variables.
Two variables must have a relationship with one another in order to define a moderator, and modifying one variable may affect the level or position of the other variable. The moderating variable in this situation will serve as a third factor and have a significant impact on how the relationship between the other two variables is shaped and directed.
The moderating variable can be in any form, it may either be a quantitative one, or a qualitative. For instance, if the moderator is a numerical variable and changes to its numerical characteristics alter the relationship of the other variables, this moderator is a quantitative variable. Such as age of the subjects, grades, height, income level, scores, etc.
However, if the moderating variable is qualitative, it will take into consideration qualitative data or qualitative characteristics of the variables. Such includes gender differences, educational differences, racial differences, ethnic differences, cultural differences, religious differences, etc.
Example of Moderator
In research on income and work experience, gender identity moderates the relationship between salary and work experience. Where:
Independent Variable: work experience
Dependent Variable: Salary
Gender is the moderator.
Purpose of Mediators and Moderators in Research
In order to get a more complete view of the real world, using mediators and moderators in your research can help you move beyond investigating a basic relationship between two variables. When examining complex correlational or causal relationships between variables, these variables are crucial to take into account.
A number of research biases, such as:
- observer bias
- survivorship bias
- under coverage bias
- omitted variable bias
These biases can be avoided or reduced by including these variables.
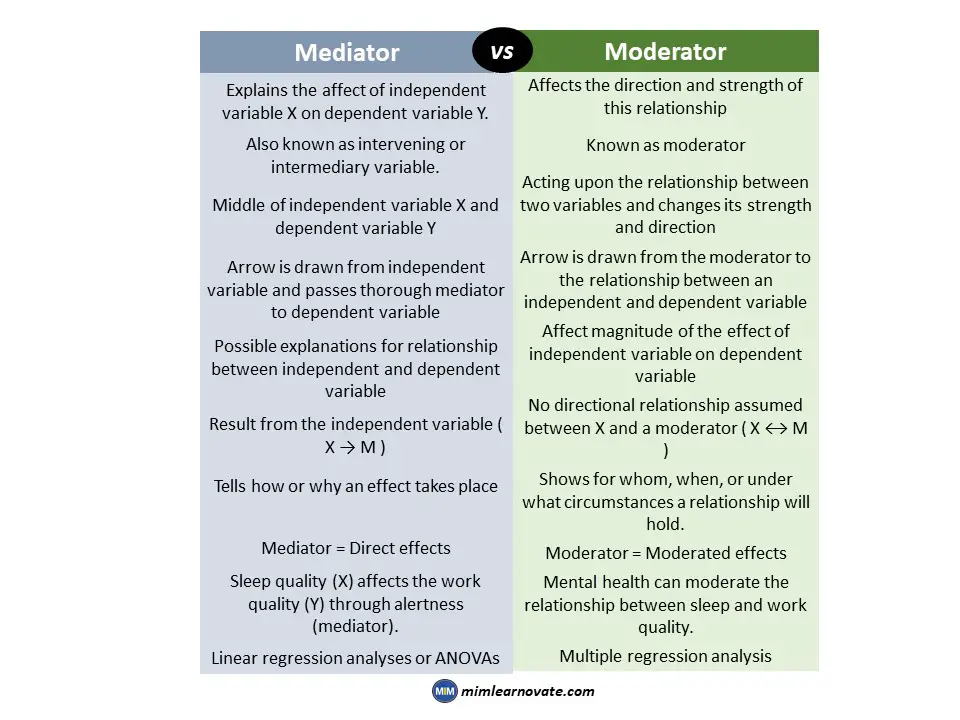
Difference between Mediator and Moderator
| Mediator | Moderator |
| Explains the affect of independent variable X on dependent variable Y. | Affects the direction and strength of this relationship |
| Also known as intervening or intermediary variable. | Known as moderator |
| Middle of independent variable X and dependent variable Y | Acting upon the relationship between two variables and changes its strength and direction |
| Arrow is drawn from independent variable and passes thorough mediator to dependent variable | Arrow is drawn from the moderator to the relationship between an independent and dependent variable |
| Possible explanations for relationship between independent and dependent variable | Affect magnitude of the effect of independent variable on dependent variable |
| Result from the independent variable ( X → M ) | No directional relationship assumed between X and a moderator ( X ↔ M ) |
| Tells how or why an effect takes place | Shows for whom, when, or under what circumstances a relationship will hold. |
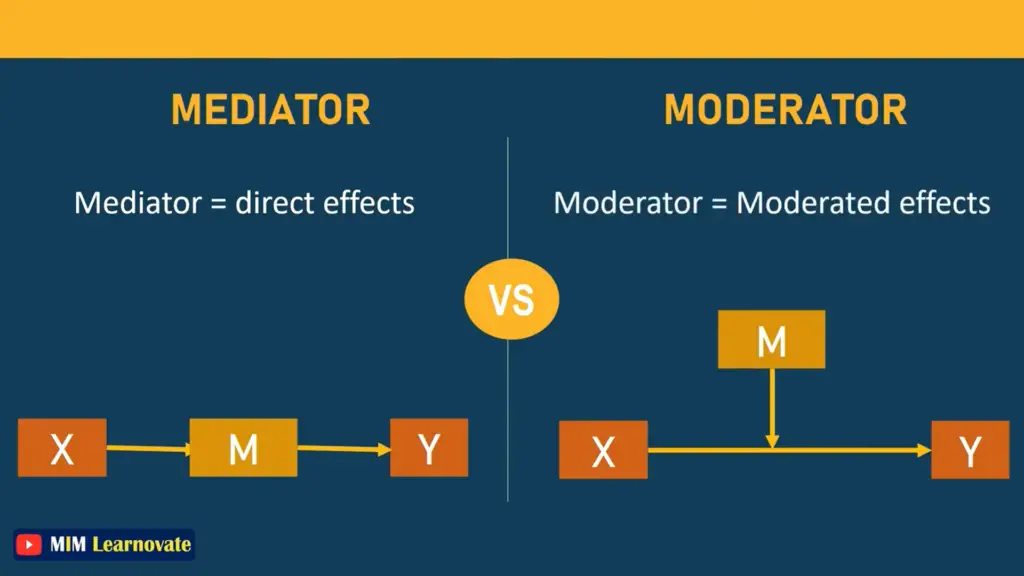
| Mediator = Direct effects | Moderator = Moderated effects |
| Sleep quality (X) affects the work quality (Y) through alertness (mediator). | Mental health can moderate the relationship between sleep and work quality. |
| Linear regression analyses or ANOVAs | Multiple regression analysis |
Difference between Mediator and Moderator
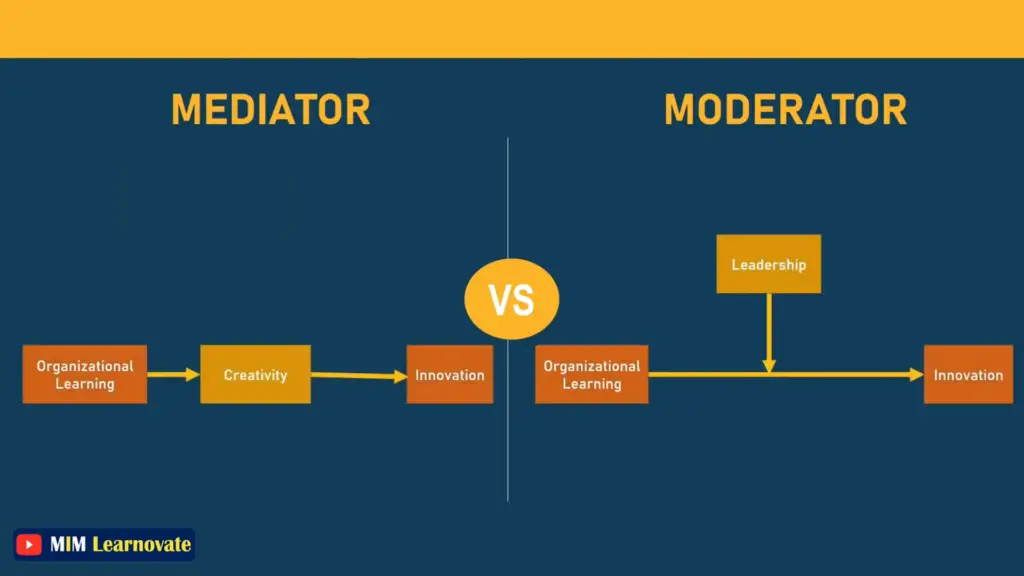
Example of Difference between Mediator and Moderator
Organization learning is independent variable and innovation is dependent variable. Let’s take creativity as a mediator because organizational learning brings creativity which will help employees to be more innovative. So, creativity is explaining the relationship between organizational learning and innovation and creativity helps to achieve innovation.
Lets add moderator between organizational learning and innovation. Take leadership as a moderator as it will strengthen the relationship of IV and DV.
Leadership influences employees to produce creative ideas, products, and services hence bringing innovation in the firm.
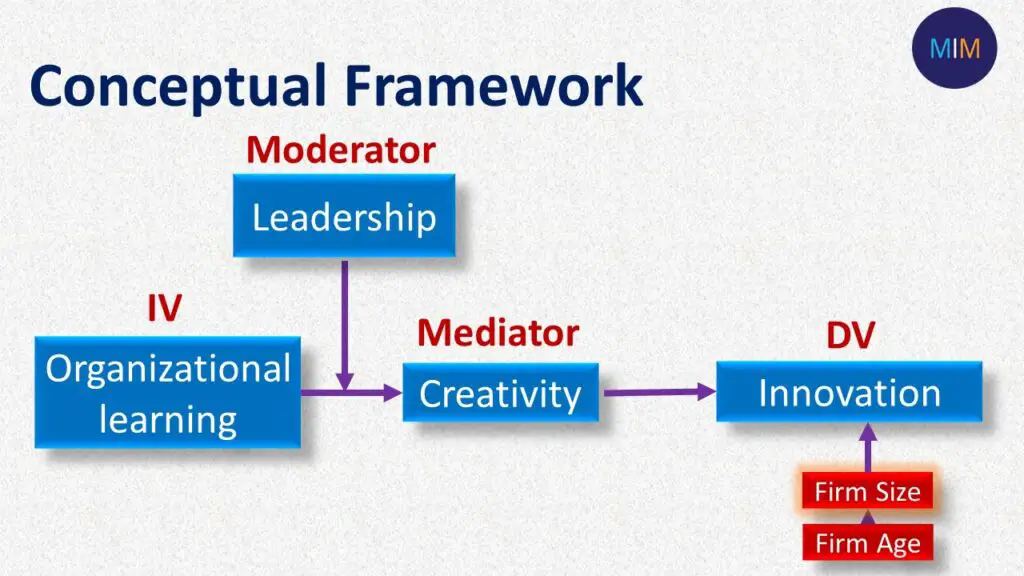
These three variables organizational learning, leadership, creativity effects innovation but there could be other variables that affects innovation like firm size and firm age.
The larger firms need to be more innovative as compared to smaller firms. So these variables by default have impact on firm’s innovation. So we should control these variables in order to see whether IV, mediator and moderator have an effect on dependent variable.
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about research methodology.
Comparision
- Basic and Applied Research
- Cross-Sectional vs Longitudinal Studies
- Survey vs Questionnaire
- Open Ended vs Closed Ended Questions
- Experimental and Non-Experimental Research
- Inductive vs Deductive Approach
- Null and Alternative Hypothesis
- Reliability vs Validity
- Population vs Sample
- Conceptual Framework and Theoretical Framework
- Bibliography and Reference
- Stratified vs Cluster Sampling
- Sampling Error vs Sampling Bias
- Internal Validity vs External Validity
- Full-Scale, Laboratory-Scale and Pilot-Scale Studies
- Plagiarism and Paraphrasing
- Research Methodology Vs. Research Method
- Mediator and Moderator
- Type I vs Type II error
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Microsoft Excel and SPSS
- Parametric and Non-Parametric Test
Comparision
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable
- Research Article and Research Paper
- Proposition and Hypothesis
- Principal Component Analysis and Partial Least Squares
- Academic Research vs Industry Research
- Clinical Research vs Lab Research
- Research Lab and Hospital Lab
- Thesis Statement and Research Question
- Quantitative Researchers vs. Quantitative Traders
- Premise, Hypothesis and Supposition
- Survey Vs Experiment
- Hypothesis and Theory
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable
- APA vs. MLA
- Ghost Authorship vs. Gift Authorship
Research
- Research Methods
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research
- Survey Research
- Conclusive Research
- Descriptive Research
- Cross-Sectional Research
- Theoretical Framework
- Conceptual Framework
- Triangulation
- Grounded Theory
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Mixed Method
- Correlational Research
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Stratified Sampling
- Ethnography
- Ghost Authorship
- Secondary Data Collection
- Primary Data Collection
- Ex-Post-Facto
Research
- Table of Contents
- Dissertation Topic
- Synopsis
- Thesis Statement
- Research Proposal
- Research Questions
- Research Problem
- Research Gap
- Types of Research Gaps
- Variables
- Operationalization of Variables
- Literature Review
- Research Hypothesis
- Questionnaire
- Abstract
- Validity
- Reliability
- Measurement of Scale
- Sampling Techniques
- Acknowledgements
Statistics



