Although premise, hypothesis, and supposition are three entirely different words, they are frequently used together. They are therefore rather confusing. How does a hypothesis relate to a premise? What does supposition mean? All of these are some of the queries asked by students.
In this article, you will learn about the difference between premise, hypothesis and supposition.
Premise
A premise is an assumption or condition that one believes to be true. Typically, it is a logical assumption or statement that is supported by some logic. A conclusion is therefore typically developed from a premise. It’s all part of logical reasoning.

Hypothesis
A statement or concept that needs to be tested in order to be proven is known as a hypothesis. Typically, it is based on known facts that have not yet been proven. It must be proved before one can consider an idea or an explanation for something to be true.

A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific process, in which an idea is typically proved through some sort of experiment or research.
Can a hypothesis be a premise?
The idea may also be referred to as a premise, which is an assumption or a condition that one holds to be true. When one attempts to prove it, it becomes a hypothesis.
Supposition
A supposition is an idea that is thought to be true, but it is uncertain whether it is exactly or to what extent. The act of supposing, imagining, or considering into account as true or existing what is known to be false or unproven.

Example of supposition
The product was introduced, for instance, under the supposition that there was a demand for it. There may be a demand for the products in this situation, but it may not be as strong as they had anticipated. As a result, the notion that there was demand may not be wrong, but rather real, but the amount is unknown.
Example: Premise vs Hypothesis vs Supposition
Premise: The ball is round.
The premise depends on what we can see and understand.
Conclusion based on the premise that the ball will roll.
On the premise, the conclusion is based. Because the ball is round, it will roll.
Hypothesis: The ball will roll 17 feet.
The hypothesis is an assertion that demands evidence. It’s possible that the ball will roll for 17 feet. In order to determine how far it will roll, it must be tested.
Supposition: This is the best ball for rolling.
The supposition is a belief. Just because the ball rolls well, you might assume that it is the best at doing so. There will undoubtedly be balls that roll better than this one, though. All the balls in the world cannot be tested to prove this. So, it might or might not be true.
This example should make it clearer how each of these words is used and how they relate to one another.
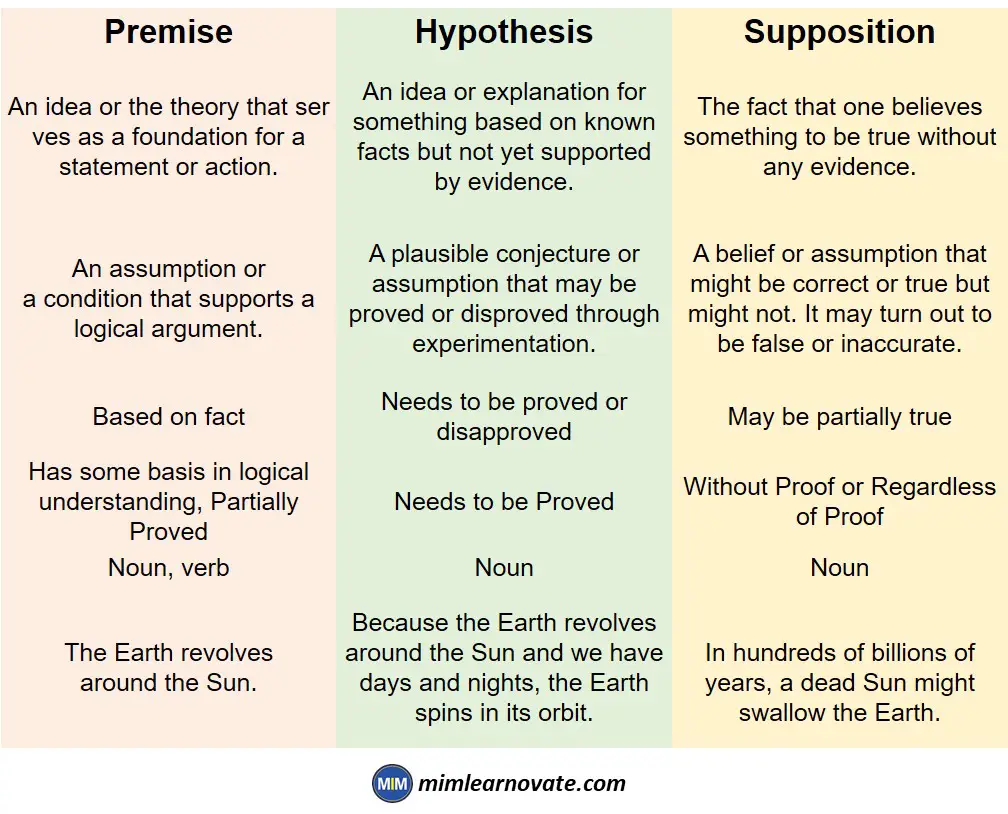
Difference between Premise, Hypothesis and Supposition
| Premise | Hypothesis | Supposition |
| An idea or the theory that serves as a foundation for a statement or action. | An idea or explanation for something based on known facts but not yet supported by evidence. | The fact that one believes something to be true without any evidence. |
| An assumption or a condition that supports a logical argument. | A plausible conjecture or assumption that may be proved or disproved through experimentation. | A belief or assumption that might be correct or true but might not. It may turn out to be false or inaccurate. |
| Based on fact | Needs to be proved or disapproved | May be partially true |
| Has some basis in logical understanding, Partially Proved | Needs to be Proved | Without Proof or Regardless of Proof |
| Noun, verb | Noun | Noun |
| The Earth revolves around the Sun. [hard fact] | Because the Earth revolves around the Sun and we have days and nights, the Earth spins in its orbit. | In hundreds of billions of years, a dead Sun might swallow the Earth. |
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about research methodology.
Citation Styles
- APA Reference Page
- MLA Citations
- Chicago Style Format
- “et al.” in APA, MLA, and Chicago Style
- Do All References in a Reference List Need to Be Cited in Text?
Comparision
- Basic and Applied Research
- Cross-Sectional vs Longitudinal Studies
- Survey vs Questionnaire
- Open Ended vs Closed Ended Questions
- Experimental and Non-Experimental Research
- Inductive vs Deductive Approach
- Null and Alternative Hypothesis
- Reliability vs Validity
- Population vs Sample
- Conceptual Framework and Theoretical Framework
- Bibliography and Reference
- Stratified vs Cluster Sampling
- Sampling Error vs Sampling Bias
- Internal Validity vs External Validity
- Full-Scale, Laboratory-Scale and Pilot-Scale Studies
- Plagiarism and Paraphrasing
- Research Methodology Vs. Research Method
- Mediator and Moderator
- Type I vs Type II error
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Microsoft Excel and SPSS
- Parametric and Non-Parametric Test
Comparision
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable – MIM Learnovate
- Research Article and Research Paper
- Proposition and Hypothesis
- Principal Component Analysis and Partial Least Squares
- Academic Research vs Industry Research
- Clinical Research vs Lab Research
- Research Lab and Hospital Lab
- Thesis Statement and Research Question
- Quantitative Researchers vs. Quantitative Traders
- Premise, Hypothesis and Supposition
- Survey Vs Experiment
- Hypothesis and Theory
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable
- APA vs. MLA
- Ghost Authorship vs. Gift Authorship
Research
- Research Methods
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research
- Survey Research
- Conclusive Research
- Descriptive Research
- Cross-Sectional Research
- Theoretical Framework
- Conceptual Framework
- Triangulation
- Grounded Theory
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Mixed Method
- Correlational Research
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Stratified Sampling
- Ethnography
- Ghost Authorship
- Secondary Data Collection
- Primary Data Collection
- Ex-Post-Facto
Research
- Table of Contents
- Dissertation Topic
- Synopsis
- Thesis Statement
- Research Proposal
- Research Questions
- Research Problem
- Research Gap
- Types of Research Gaps
- Variables
- Operationalization of Variables
- Literature Review
- Research Hypothesis
- Questionnaire
- Abstract
- Validity
- Reliability
- Measurement of Scale
- Sampling Techniques
- Acknowledgements
Statistics
- PLS-SEM model
- Principal Components Analysis
- Multivariate Analysis
- Friedman Test
- Chi-Square Test (Χ²)
- T-test
- SPSS
- Effect Size
- Critical Values in Statistics
- Statistical Analysis
- Calculate the Sample Size for Randomized Controlled Trials
- Covariate in Statistics
- Avoid Common Mistakes in Statistics
- Standard Deviation
- Derivatives & Formulas
- Build a PLS-SEM model using AMOS
- Principal Components Analysis using SPSS
- Statistical Tools
- Type I vs Type II error
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Microsoft Excel and SPSS
- One-tailed and Two-tailed Test
- Parametric and Non-Parametric Test



