Modern research is different from traditional research in a number of ways, mostly because of technological developments, changes to research methods, and evolving societal needs.
Modern Research vs Traditional Research
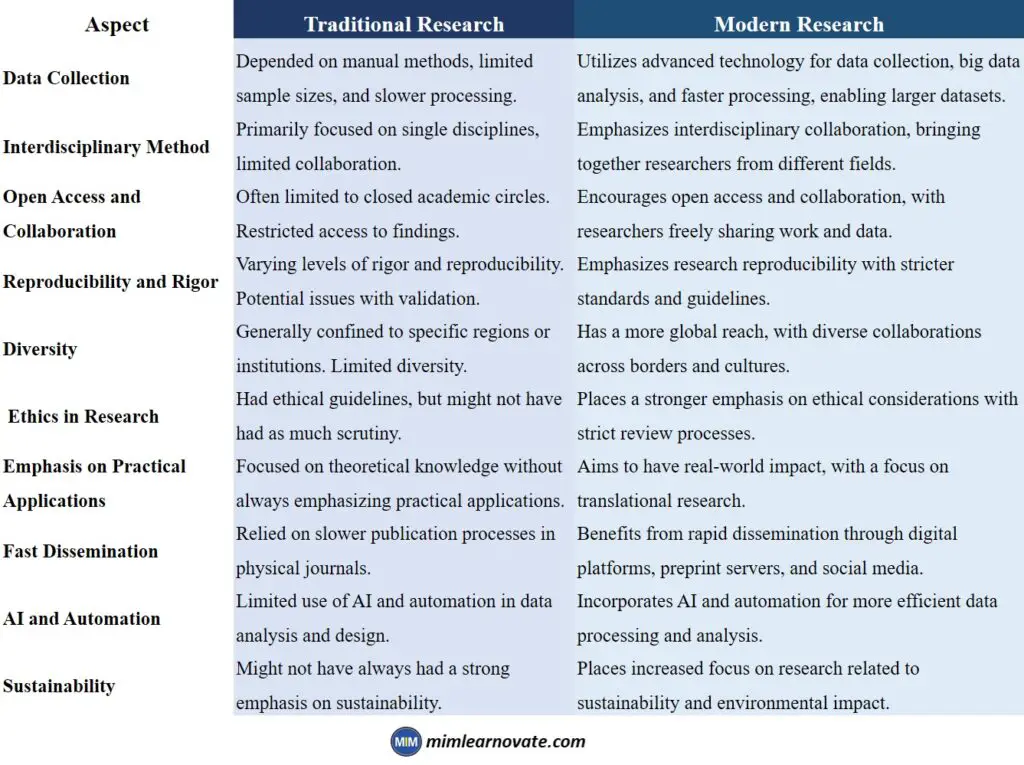
| Aspect | Traditional Research | Modern Research |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Depended on manual methods, limited sample sizes, and slower processing. | Utilizes advanced technology for data collection, big data analysis, and faster processing, enabling larger datasets. |
| Interdisciplinary Method | Primarily focused on single disciplines, limited collaboration. | Emphasizes interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together researchers from different fields. |
| Open Access and Collaboration | Often limited to closed academic circles. Restricted access to findings. | Encourages open access and collaboration, with researchers freely sharing work and data. |
| Reproducibility and Rigor | Varying levels of rigor and reproducibility. Potential issues with validation. | Emphasizes research reproducibility with stricter standards and guidelines. |
| Diversity | Generally confined to specific regions or institutions. Limited diversity. | Has a more global reach, with diverse collaborations across borders and cultures. |
| Ethics in Research | Had ethical guidelines, but might not have had as much scrutiny. | Places a stronger emphasis on ethical considerations with strict review processes. |
| Emphasis on Practical Applications | Focused on theoretical knowledge without always emphasizing practical applications. | Aims to have real-world impact, with a focus on translational research. |
| Fast Dissemination | Relied on slower publication processes in physical journals. | Benefits from rapid dissemination through digital platforms, preprint servers, and social media. |
| AI and Automation | Limited use of AI and automation in data analysis and design. | Incorporates AI and automation for more efficient data processing and analysis. |
| Sustainability | Might not have always had a strong emphasis on sustainability. | Places increased focus on research related to sustainability and environmental impact. |
1. Use of Technology in Data Collection
Larger sample sizes and more comprehensive datasets are made possible by the use of advanced technology in modern research, which makes data collection faster, more accurate, and efficient. Examples of these technologies include digital sensors, online surveys, and big data analysis.
Traditional Research: Depended on manual data collection methods, limited sample sizes, and slower data processing.
Modern Research: Uses advanced technology for data collection, big data analysis, and faster processing, enabling larger and more comprehensive datasets.
2. Collaboration
Open access to study results and data is becoming increasingly important in modern research. Researchers can openly share their work through collaborative platforms and open-source initiatives, which speeds up the pace of discovery and promotes transparency.
Traditional Research: Often limited to closed academic circles, with restricted access to research findings and data.
Modern Research: Encourages open access and collaboration, with researchers freely sharing their work and data to accelerate discoveries.
3. Interdisciplinary Method
Modern research benefits from technological advancements that make data collection faster, more accurate, and efficient. To collect and process data, researchers can now use digital sensors, online surveys, and big data analysis. This allows for larger sample sizes and more comprehensive datasets.
Traditional Research: Primarily focused on single disciplines, with limited collaboration across fields.
Modern Research: Emphasizes interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together researchers from different disciplines to address complex problems.
rigor and reproducibility
In modern research, rigor and reproducibility of findings are becoming increasingly important. To ensure that research findings can be independently validated and lower the possibility of producing incorrect or misleading results, stricter criteria and guidelines have been put in place.
Traditional Research: Had varying levels of rigor and reproducibility, leading to potential issues with validation.
Modern Research: Emphasizes research reproducibility, with stricter standards and guidelines to ensure reliable and verifiable results.
5. Diversity
Research nowadays is becoming diverse and worldwide. By working together across national boundaries, cultural barriers, and personal experiences, researchers broaden the scope of their scientific investigations.
Traditional Research: Generally confined to specific geographic regions or institutions, limiting diversity of perspectives.
Modern Research: Has a more global reach, with researchers collaborating across borders and cultures, leading to diverse viewpoints.
6. Ethics in Research
Although ethics have always been important in research, they are given greater importance in modern research. Stricter ethical guidelines and approval procedures apply to research involving humans or animals.
Traditional Research: Had ethical guidelines but might not have had as much scrutiny as modern research.
Modern Research: Places a stronger emphasis on ethical considerations, with strict review processes for research involving human subjects or animals.
7. Emphasis on Practical Applications
Modern research frequently seeks to have effects and applications that are useful in the real world. Translational research that can be used immediately to solve societal issues and enhance people’s lives is becoming more and more important.
Traditional Research focuses on theoretical knowledge without always emphasizing practical applications.
Modern Research: Aims to have real-world impact, with a focus on translational research and solutions to address societal challenges.
8. Sustainability
Modern research frequently looks for answers to ecological problems, alternate energy sources, and solutions to slow down climate change because of the growing concern about sustainability and its effects on the environment worldwide.
Traditional Research: Might not have always had a strong emphasis on sustainability-related issues.
Modern Research: Places increased focus on research related to sustainability, environmental impact, and climate change.
9. Fast Dissemination
The internet has made it possible for research findings to be quickly shared through a variety of platforms. Preprint servers, social media, and online journals facilitate the rapid dissemination of research findings and the prompt acquisition of community response.
Traditional Research: Relied on slower publication processes in physical journals.
Modern Research: Benefits from rapid dissemination through digital platforms, preprint servers, and social media.
10. Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Automation and artificial intelligence are useful in modern research when it comes to data analysis, literature reviews, and experimental design. Large volumes of data could be processed by AI algorithms, which can also spot patterns that humans will overlook.
Traditional Research: Limited use of AI and automation in data analysis and experimental design.
Modern Research: Incorporates AI and automation for more efficient data processing and analysis.
Conclusion
Increased productivity, teamwork, interdisciplinary approaches, and a greater focus on practical applications and ethical issues are characteristics of modern research.
Technological developments and a rising understanding of the significance of addressing complex global issues are the driving forces behind these changes.
Other articles
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about research methodology.
Comparision
- Basic and Applied Research
- Cross-Sectional vs Longitudinal Studies
- Survey vs Questionnaire
- Open Ended vs Closed Ended Questions
- Experimental and Non-Experimental Research
- Inductive vs Deductive Approach
- Null and Alternative Hypothesis
- Reliability vs Validity
- Population vs Sample
- Conceptual Framework and Theoretical Framework
- Bibliography and Reference
- Stratified vs Cluster Sampling
- Sampling Error vs Sampling Bias
- Internal Validity vs External Validity
- Full-Scale, Laboratory-Scale and Pilot-Scale Studies
- Plagiarism and Paraphrasing
- Research Methodology Vs. Research Method
- Mediator and Moderator
- Type I vs Type II error
- Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Microsoft Excel and SPSS
- Parametric and Non-Parametric Test
Comparision
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable – MIM Learnovate
- Research Article and Research Paper
- Proposition and Hypothesis
- Principal Component Analysis and Partial Least Squares
- Academic Research vs Industry Research
- Clinical Research vs Lab Research
- Research Lab and Hospital Lab
- Thesis Statement and Research Question
- Quantitative Researchers vs. Quantitative Traders
- Premise, Hypothesis and Supposition
- Survey Vs Experiment
- Hypothesis and Theory
- Independent vs. Dependent Variable
- APA vs. MLA
- Ghost Authorship vs. Gift Authorship
Research
- Research Methods
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research
- Survey Research
- Conclusive Research
- Descriptive Research
- Cross-Sectional Research
- Theoretical Framework
- Conceptual Framework
- Triangulation
- Grounded Theory
- Quasi-Experimental Design
- Mixed Method
- Correlational Research
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Stratified Sampling
- Ethnography
- Ghost Authorship
- Secondary Data Collection
- Primary Data Collection
- Ex-Post-Facto
Research
- Table of Contents
- Dissertation Topic
- Synopsis
- Thesis Statement
- Research Proposal
- Research Questions
- Research Problem
- Research Gap
- Types of Research Gaps
- Variables
- Operationalization of Variables
- Literature Review
- Research Hypothesis
- Questionnaire
- Abstract
- Validity
- Reliability
- Measurement of Scale
- Sampling Techniques
- Acknowledgements
Statistics



